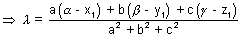3D Geometry - 2
Illustration: Find angle b/w lines whose direction cosines are 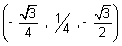 &
& 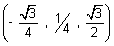 .
.
Ans: Let 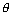 be angle
be angle
cos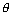 = l1l2 + m1m2 + n1n2
= l1l2 + m1m2 + n1n2
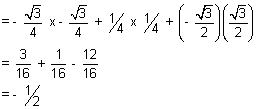
cos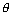 = -
= - 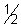
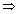
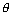 = 1200
= 1200
Straight line:
Vectorial eq. of line:
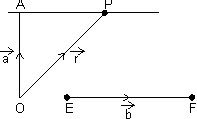
Let a line passing through a point of P.V.
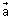 & || to given line EF(
& || to given line EF(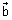 ).
).Then, eq. of line
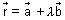
Proof: Let P be any point on line AP & its P.V. is
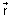
Then,
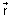 =
= 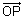 =
= 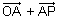 (By
(By  law)
law)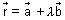
Dumb Question: Why
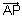 =
= 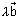 ?
?Ans: Since
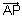 is || to EF of P.V.
is || to EF of P.V.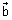
So,
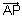 =
= 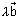
Note: Eq. of line through origin & || to
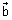 is
is 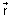 =
= 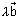
Cartesion eq. of straight line:
Passing through point & parallel to given vector .
Let line is passing through A(x1, y1, z1) & || to EF whose d.r.'s are a, b, c.
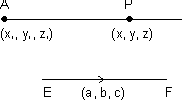
d.r.'s of AP = (x - x1, y - y1, z - z1)
d.r.'s of EF = (a, b, c)
Since EF || AP, then,
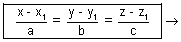 b Eq. of line in parametric form.
b Eq. of line in parametric form.Illustration: Find eq. of line || to
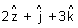 & passing through pt.(1, 2, 3) ?
& passing through pt.(1, 2, 3) ?Ans: A(1, 2, 3)
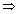
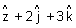 =
= 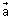
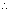 eq. of line passing through
eq. of line passing through 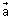 & || to
& || to 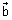
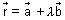 = (
= (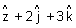 ) +
) + 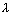 (
(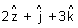 )
)Vector eq. of line passing through two given points:
Vector eq. of line passing through two points whose P.V. S
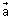 &
& 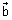 is:
is: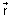 =
= 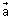 +
+ 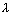 (
(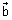 -
- 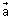 )
)Proof:
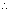
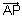 is collinear with
is collinear with 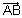
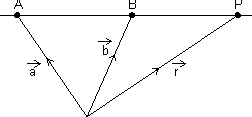
 =
= 
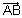
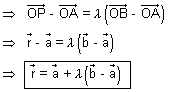
Cartesian form:
Eq. of line passing through (x1, y1, z1) & (x2, y2, z2)
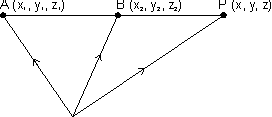
D.R.'s of AB = (x2 - x1, y2 - y1, z2 - z1)
D.R.'s of AP = (x - x1, y - y1, z - z1)
Since AB || AP
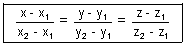
Illustration: Find cartesian eq. of line are 6x + 2 = 3y - 1 = 2z + 2. Find its direction ratios.
Ans:
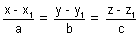 is cartesion eq. of line
is cartesion eq. of line6x + 2 = 3y - 1 = 2z + 2
6(x +
 ) = 3(y -
) = 3(y -  ) = 2(z + 1)
) = 2(z + 1)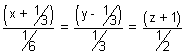
on comparing a =
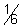 , b =
, b = 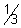 , c =
, c = 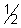
Angle b/w Two lines:
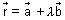
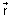 =
= 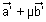
Angle b/w two lines cos
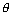 =
= 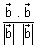
If
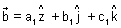
=
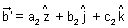
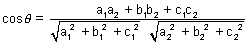
Condition for perpendicularity:
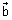 .
. = 0
= 0  a1a2 + b1b2 + c1c2
a1a2 + b1b2 + c1c2Condition for parallelism:
Dumb Question: Why angle between pair of lines
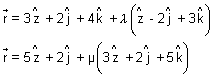
Ans:
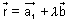 &
& 
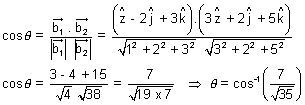
Perpendicular distance of point froma line:
(a) Castesian form:
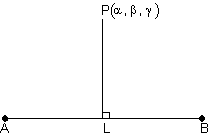
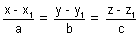
Suppose 'L' is foot of line of
 .
.Since L lies on line AB so,
coordinate of L is
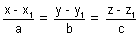 =
= 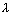
i.e. L(x1 +
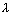 a, y1 +
a, y1 + 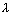 b, z1 +
b, z1 + 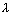 c)
c)direction ratios of PL are:
(x1 +
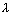 a -
a - 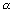 , y1 +
, y1 + 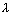 b -
b - 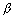 , z1 +
, z1 + 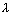 c -
c - 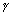 )
)also direction ratios of AB are (a, b, c)
Since PL
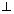 AB
AB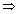 a(x1 +
a(x1 + 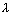 a -
a - 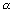 ) + b(
) + b(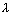 b -
b - 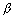 ) + c(z1 +
) + c(z1 + 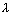 c -
c - 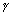 ) = 0
) = 0