Acid - Derivatives-3
Acid derivatives
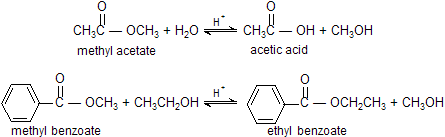
CH3COOC2H5 Ethylacetate
Preparation
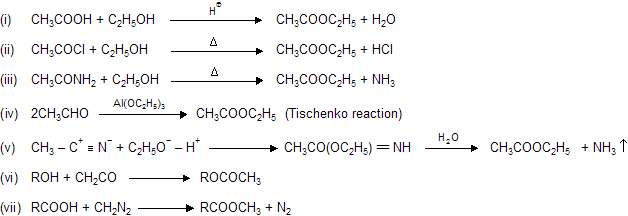
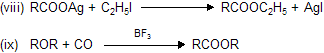
Properties
(i) Hydrolysis of esters
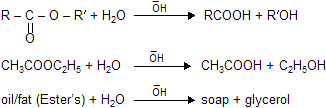 |
Oil or fats are glycerides of higher fatty acid and when they undergo hydrolysis soaps are formed in presence of alkali is known as saponification.
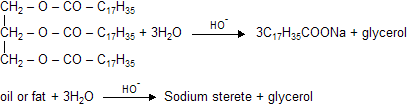 |
(ii) Trans–esterification
Esters do not undergo substitution reaction with halide ions or with carboxylate ions because these nucleophiles are much weaker bases than the RO- leaving group of the ester. Esters react with water to form carboxylic acids and with alcohols to form different esters. A reaction with water is known as hydrolysis, and a reaction with an alcohol is called alcoholysis. The hydrolysis or alcoholysis of an ester is a very slow reaction. Therefore, when these reactions are carried out in the laboratory, they are always catalyzed. Both hydrolysis and alcoholysis of an ester can be catalyzed by acids (H+). The rate of hydrolysis can also be increased by hydroxide ion (HO-), and the rate of alcoholysis can be increased by presence of alkoxide ion.