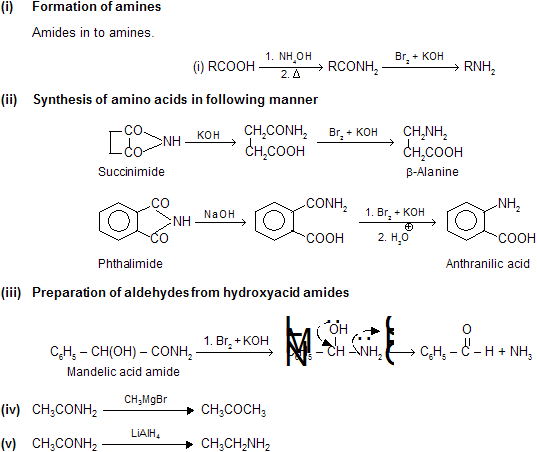
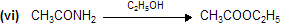Acid Derivatives -2
Preparation
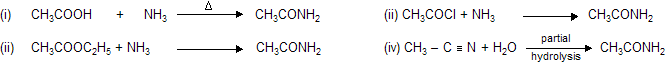
Properties
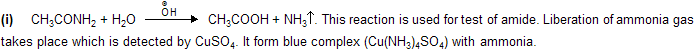
(ii) Hofmann Hypobromite Reaction
The reaction involves the conversion of an amide into a primary amine with one less carbon, by the action of alkaline hypohalite (NaOH solution + Br2 or Cl2). The overall reaction is
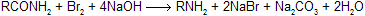
where R may be aliphatic, aromatic or heterocyclic, reaction is used for degradation of amines in homologous series.
Mechanism of reaction
Following mechanism has been suggested on the basis of the intermediates formed during the course of reaction.
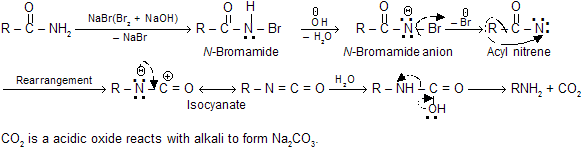
It is important to note that there is no cross-over products are obtained when two different amides are rearranged. It is assumed that the rearrangement is intramolecular and the migrating group never completely separates from each other during the migration.
This is further confirmed by the fact that if R is chiral (asymmetric), it migrates with unchanged configuration. Thus, camphoramidic acid (A) having the COOH and CONH2 groups in cis position undergoes Hofmann rearrangement to give the amino acid (B) in which the COOH and NH2 groups are also in cis position, since it readily forms lactam by removal of water.
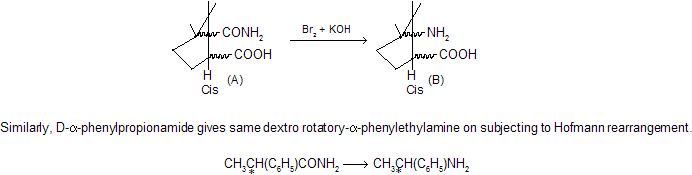
Remember, in this chemical reaction rate of reaction increases when the migrating group is more electron-donating and decreases when electron-attracting. If R is an alkyl group with more than eight carbons, low yields are obtained.
This chemical reaction is used for degradation of amines homologous series.
Applications