Acid derivatives - 1
Acid derivatives
Introduction
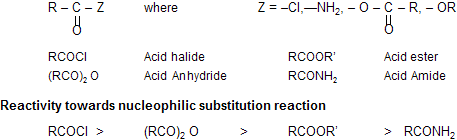
Nucleophilic Substitution : Alkyl vs. Acyl
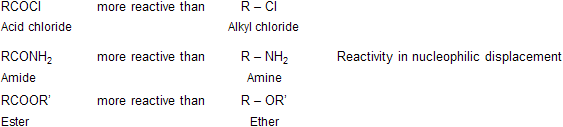
As we have said, nucleophlic substitution takes place much more readily at an acyl carbon than at saturated carbon. Thus, toward nucleophilic attack acid chlorides are more reactive than alkyl chlorides, amides are more reactive than amines and esters are more reactive than ether.
It is, of course, the carbonyl group that makes acyl compounds more reactive than alkyl compounds. Nucleophilic attack (SN2) on a tetrahedral alkyl carbon involves a badly crowded transition state containing pentavalent carbon ; a bond must be partly broken to permit the attachment of the nucleophile :
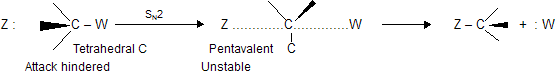
Nucleophilic attack on a flat acyl compound involves a relatively unhindered transition state leading to a tetrahedral intermediate that is actually a compound; since the carbonyl group is unsaturated, attachment of the nucleophile requires Acyl nucleophilic substitution
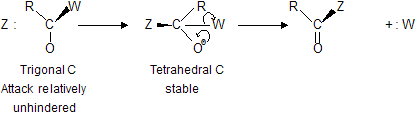 |
breaking only of the weak
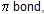 and places a negative charge on an atom quite willing to accept its, oxygen.
and places a negative charge on an atom quite willing to accept its, oxygen.