Alcohol-Diol-Triol-3
(10) From epoxides
Although the chemical reactions of epoxides will not be covered in detail until the following chapter, we shall introduce their use in the synthesis of alcohols here.
Grignard reagents react with ethyleneoxide to yield primary alcohols containing two more carbon atoms then the alkyl halide from which the organometallic compound was prepared epoxides are open by charge separation of carbon and oxygen, then attach with grignard reagent.
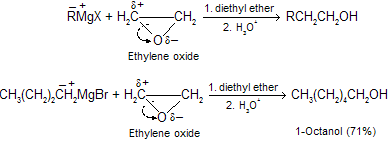
Organolithium reagents react with epoxides in a similar manner. These reactions are used to convert lower alcohol into higher alcohol.
Puzzle: Prepared the following compounds by the help of tetrahydrofuran.
(1) Succinic acid (2) adipic acid (3) Glutaric acid
| Solution: | 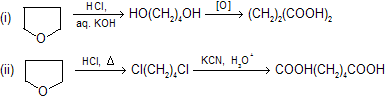 |
Epoxide rings are readily opened with cleavage of the carbon-oxygen bond when attacked by serving as sources of nucleophilic carbon so this method can also be used for stepping up to two carbon atom. For example
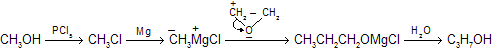
This kind of chemical reactivity of epoxides is rather general. Nucleophiles other than Grignard reagents react with epoxides, and epoxides more elaborate than ethylene oxide may be used.
Reactions of alcohols :
Alcohols are versatile starting materials for the preparation of a variety of organic functional groups. Several reactions of alcohols have already been seen in earlier chapters and are summarized in Table .
Alcohols can undergo reactions involving various combinations of the bonds of carbon and oxygen. The ionization of alcohols when they act as weak acids and the formation of alkoxides when they react with metals are reactions that take place at the O–H bond.
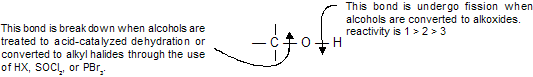
The carbon-oxygen bond of alcohols is cleaved when alcohols are converted to alkyl halides or undergo acid-catalyzed dehydration.
Some of the new reaction of alcohols that we will examine in this chapter occur by O–H bond breaking and some by C–O bond breaking. Additionally, primary and secondary alcohols can exhibit a third reaction type in which a carbon-oxygen double bond is formed by cleavage of both an O–H bond and a C–H bond:
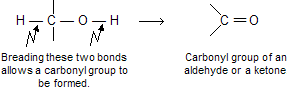
Chemical properties of alcohol
(i) Acidic nature of alcohol
Even alcohol are neutral to litmus and do not reacts with alkali like NaOH but contain active hydrogen atom so reacts with Na or K metal.
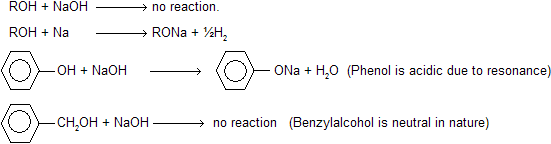
reactivity of alcohol towards metal 1° > 2° > 3° alcohol