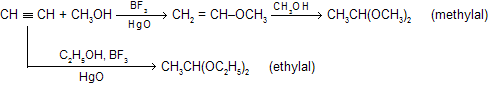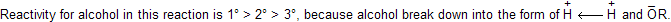Alcohol-Diol-Triol-4
(ii) Reaction with Thionyl chloride and phosphorus Halides
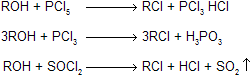
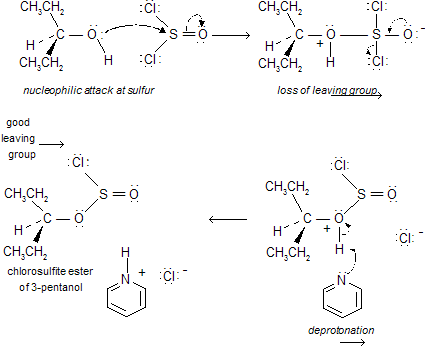
Other reagents can also be used to avoid carbocation intermediates and minimize rearrangements in the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides. One of these is thionyl chloride, SOCl2. 3-Pentanol will react with thionyl chloride in pyridine to give 3-chloropentane, and no 2-chloropentane.
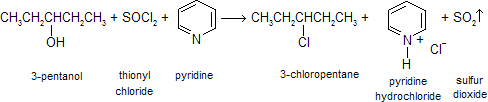
This reaction is often accompanied by elimination reactions, so it does not give high yields and a good leaving group. An intermediate chlorosulfite ester, which decomposes to give the alkyl halide. In the presence of organic bases such as pyridine, inversion of configuration is seen for chiral compounds.
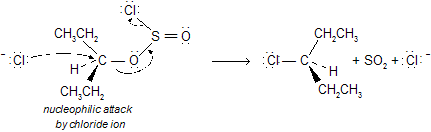
Another reagent that is used to substitute a halogen for a hydroxyl group with a minimum of rearrangement is phosphorus tribromide. For example, it is used to convert the primary alcohol isobutyl alcohol into isobutyl bromide.
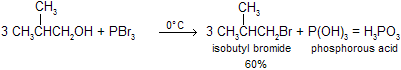
The mechanism suggested for the conversion of an alcohol to an alkyl halide using phosphorus tribromide resembles the one proposed for the conversion using thionyl chloride. Its first step is the formation of a phosphorus- oxygen bond between the alcohol and phosphorus tribromide, giving a phosphorus ester that has a good leaving group.
(iii) Reaction of alcohol with Hydrogen Halides
Alkyl halides, which participate in many different substitution reactions, may be prepared from alcohols in different ways. The hydroxyl group in an alcohol can be converted into a good leaving group so that it can be displaced by an incoming halide ion. For example, dissolving gaseous hydrogen bromide in 1-heptanol converts the alcohol to 1-bromoheptane.
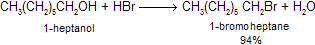
(iv) Haloform test only for 2–alkanone (by three equivalents of halogen)
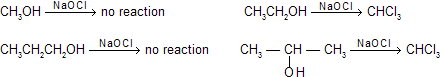
(v) Dehydration of alcohols
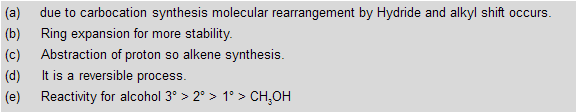
Alcohols when are reacts with any dehydrating reagent to form alkenes with removal of water. Intermediate carbocation formation takes place where rearrangement occurs by alkyl shift, hydride shift and ring expansion.
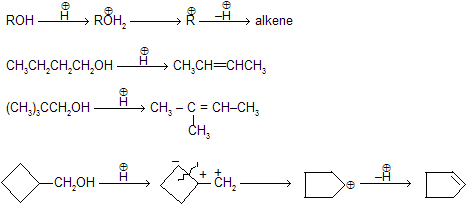
In smaller ring always ring expansion takes place due to molecular strain and they tends to convert to high stability with large ring.
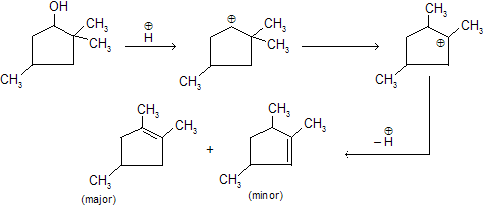
In Dehydration of alcohols
(vi) Alcoholation of alkyne
When alcohols reacts with alkyne in the presence of BF3 and HgO, according to markonikoff’s rule they forms ethers.