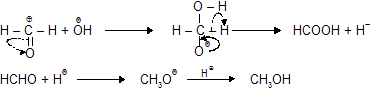Aldehydes-Ketones-3
(ii) Aldol Condensation
Aldehydes or ketones with ![]() when treated with dilute alkali like NaOH,K2CO3 etc. undergo nucleophilic addition by active intermediate carbanion to form
when treated with dilute alkali like NaOH,K2CO3 etc. undergo nucleophilic addition by active intermediate carbanion to form ![]() known as aldols.
known as aldols.
Various basic reagents such as potassium hydroxide, aqueous alkali carbonate, alkali metal alkoxides, etc., may be used. The reaction is not favourable for all type of ketones but applicable in some special cases like CH3COCH3.
Aldol condensation are of different type and it can occur between
| (i) two identical or different aldehydes, | |
| (ii) two identical or different ketones and | |
| (iii) an aldehyde and a ketone. |
When the condensation is between two different carbonyl compounds, it is called crossed aldol condensation.
(a) Simple Aldol
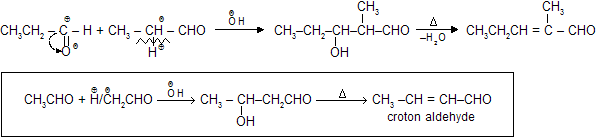
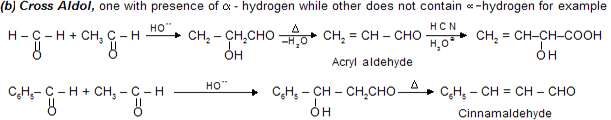
Above reaction is also called as Claisen Schimdt Condensation where one is aromatic carbonyl compound and other is aliphatic carbonyl compound.
In cross aldol condensation possibility of more than one product is always there so these reactions are not very much useful for synthatic chemistry. For example :
Acetone can also undergo aldol type reaction in the presence of dilute alkali (base catalyst) or dry HCl gas.
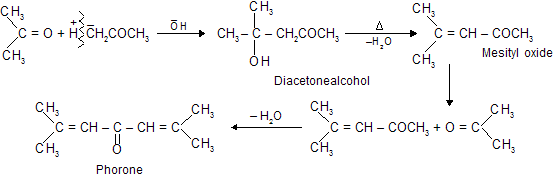
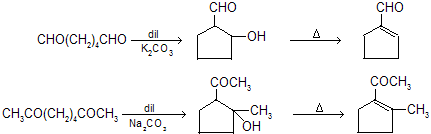
Intraaldol condensation: Dicabonyl compounds, having two carbonyl groups within the same molecule, undergo intramolecular aldol condensation reactions. Even bases as weak as sodium carbonate are adequate in these reactions.
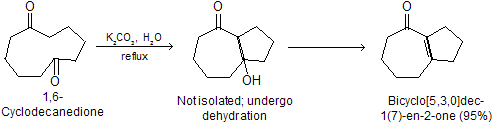
Intramolecular aldol condensations proceed best when five- or six- membered rings result because these are of minimum strain ring.
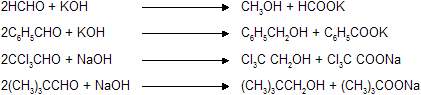
(iii) Cannizaro’s Reaction
Aldehydes which do not have any![]() , when treated with concentrated solution of NaOH or KOH, undergo simultaneous oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) forming a salt of carboxylic acid and alcohol.
, when treated with concentrated solution of NaOH or KOH, undergo simultaneous oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) forming a salt of carboxylic acid and alcohol.
Here 'R' should be –H or phenyl but not alkyl group with presence of ![]() .
.
In the presence of a high concentration of base, the reaction follows fourth-order law (second order in both two molecules of base), i.e., rate
The hydride ion is directly transferred from one molecule of the aldehyde to the other, and does not become free in solution has been proved by the observation that the recovered alcohol does not contain deuterium when the reaction is performed in the presence of D2O.
Cannizaro Reaction of HCHO
Transfer of hydride ion due to back donation of oxygen charged electron give out hydride ion which is used for reduction of other carbonyl molecule so oxidation of one molecule gives acid salt while other by reduction forms alcohol.
(a) Simple cannizaro's reaction