Alkanes-Paraffins-1
Alkanes Paraffins
chapter
General formula of alkanes is Cn H2n+2
They are also called paraffins (parum = Little + affinis = reactivity).
They may have no bond polarity and does not contain
 in the molecule so known as saturated hydrocarbons.
in the molecule so known as saturated hydrocarbons.Preparation
(i) From Grignard reagent
RMgX alkyl magnesium halide (other examples of RMgX type molecules are RLi and R2Cd)
This reaction is known as Zere wittinoff’s method for estimation of active hydrogen in the molecule. Active hydrogen is the one which is attached to a highly electronegative element. eg., N,O,S etc. Hydrogen attached to alkyl groups like —CH3, —C2H5 are never active due to less electronegativity of ‘C’ atom.
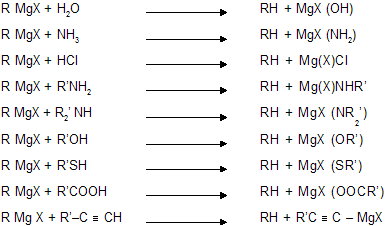
R’ in Hydrocarbon always comes from grignard reagent. In case of alkynes, only 1-alkynes reacts with G.R because it contains active Hydrogen atom attached with a ‘sp’ hybridized carbon atom with maximum electronegativity.
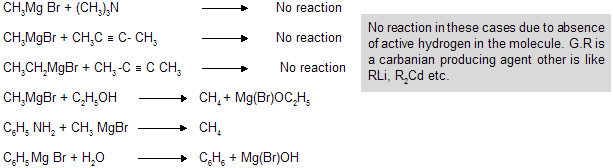
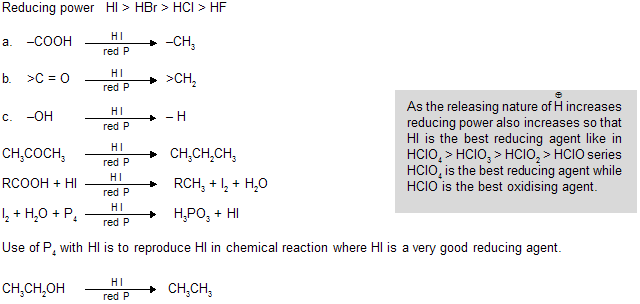
(ii) From HI and red phosphorous