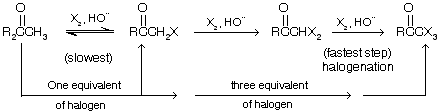Alkyl-Halides-1
Alkyl Halides
Trihalogen Derivatives
The general formula of trihalogen derivative is CHX3
These are also called HALOFORMS.
Preparation
(i) Haloform test is given by compounds having –COCH3 group.
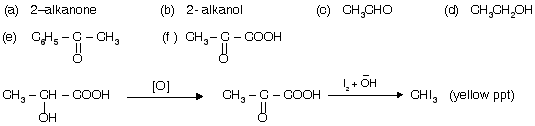
CH3COOH cannot give haloform test due to resonance and does not contain pure COCH3 group.
C6H5COC6H5 Benzophenone does not give haloform test due to absence of –COCH3 group.
 | 2-alkanol but cannot give haloform test because it is inert towards first step oxidation. |
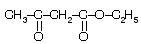 | Acetoacetic ester even though contains –COCH3 group but does not give haloform test due to active methylene group in the molecule where first halogenation occurs. |
The reacting compounds for haloform test are halogen and alkali which are responsible for halogenation, oxidation and hydrolysis.
Reactions involved in haloform test are :
(a) Oxidation (b) Halogenation (3 equivalent) (c) Hydrolysis in presence of base
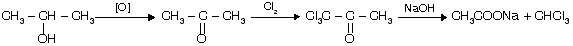
Halogen and alkali are used as they form OQ Cl or hypohalite ion which is a strong base to replace all 3-‘H’

The haloform reaction
Halogenation of the µ- carbon atom takes place when an enolate ion is generated in the presence of chlorine, bromine, or iodine (any halogen).
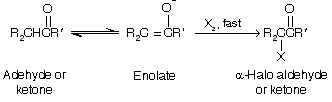
In the acid-catalyzed halogenation of aldehydes and ketones, rate is independant of the concentration of the halogen; chlorination, bromination, and iodination all at the same rate. Formation of the enolate is rate-determining, and once formed the enolate ion reacts rapidly with the halogen but remember three equivalents are required for haloforms.
Unlike its acid-catalyzed route, a-halogenation in base catalysed cannot normally be limited at monohalogenation. Methyl ketones, for example, undergo polyhalogenation and cleavage on treatment with a halogen in aqueous base.
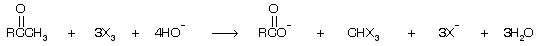
This is called the haloform reaction because the trihalomethane produced is chloroform, bromoform, or iodoform depending, of course, on the halogen used. Remember this reaction is done by three equivalent of halogen but if there is only one equivalent of halogen then mono halo product is formed.
Normally in seperation test of 2-alkanol or 2-alkanone with other alkanol or alkan one we prefer I2 and alkali for test because formation of yellow ppt of CHI3 takes place.
The mechanism of first phase of the haloform reaction begin with a-halogenation through the enolate. The electron-attracting –I effect of an a-halogen increases the acidity of the protons on the carbon to which it is bonded, making each H active and undergo halogenation at that carbon faster than the preceding one.