Alkynes-4
Because alkynes possess only limited solubility in aqueous sulphuric acid so methanol or acetic acid are added as a cosolvent.
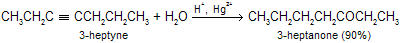
Hydration of alkynes follows Markovnikov’s rule; terminal alkynes yield methyl substituted ketones.

Because of the regioselectivity of alkyne hydration, acetylene is the only alkyne structurally capable of yielding an aldehyde under these conditions but not give good yield.
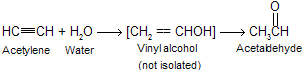
(iv) Reaction with CH3COOH
This method is just opposite to hydroboration oxidation process where product are formed just opposite to these one. At one time acetaldehyde was prepared on an industrial scale by this method. More modern methods involve direct oxidation of ethylene and are more economical like Wacker process (oxidation by PdCl2 and air)
(iv) Reaction with CH3COOH

Poly vinyl acetate is used as adhesive. When poly vinyl acetate undergoes hydrolysis it forms poly vinyl alcohol which works as industrial solvent and remember poly vinyl alcohol cannot be obtained by polymerisation of vinyl alcohol.
(v) Reaction with HCl

(vi) Reaction with HCN

(vii) Alkynylation of carbonyl compounds
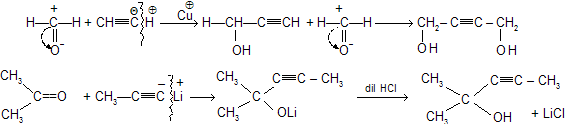
When 1-alkynes in the presence of metal reacts with carbonyl compound is known as Alkynylation of carbonyl compound, forms unsaturated alcohols.
(viii) Hydroboration followed by oxidation
Over all reaction is addition of water anti to the Markovnikov’s’s rule and produces aldehydes or ketones depends on alkyne structure (mechanism is similar that we follow in alkenes)
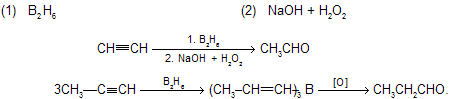
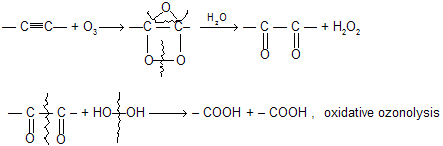
(ix) Ozonolysis (1) O3 (2) H2O