application-of-derivatives-2
Dumb Question: How this derived ?
Ans: Let m1 = tan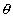 1 =
1 = 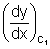
m2 = tan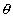 2 =
2 = 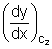
From fiq, 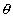 =
= 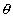 +
+ 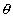 1
1
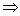
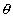 =
= 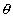 2 -
2 - 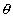 1
1
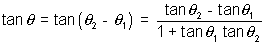
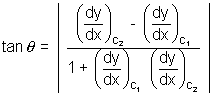
Orthogonal curves: If angle of intersection of two curves is right angle, two curves are c/d orthogonal curves.
If curves are orthogonal, 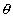 =
= 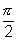
Illustration: Find angle of intersection of curves y = x2 & y = 4 - x2
For intersection points of given curves,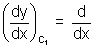 (x2) = 2x
(x2) = 2x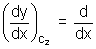 (4 - x2) = - 2x
(4 - x2) = - 2x
At x = - 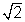 ,
,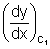 = 2 x
= 2 x 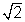 = 2
= 2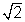 &
& 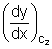 = - 2
= - 2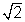
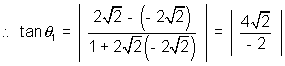
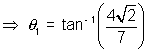
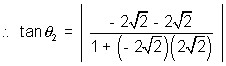
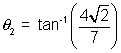
Both angles are equal.
Length of Tangent, Sub-Tangent, Normal & sub-Normal:
Length of Tangent: Length of segment PT of tangent b/w point of tangent & x-axis is c/d length of tangent.
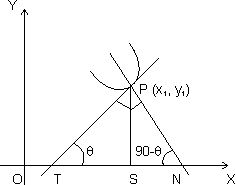
PT =
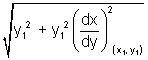
Subtangent: Projection of segment PT along x-axis i.e. St c/d subtangent.
Length of Normal: Length of segment PN intercapted b/w point on curve r x-axis.
PN =
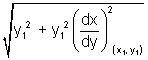
Subnormal: Projection of segment PN along x-axis i.e. c/d subnormal.
SN = |y,
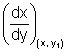
Dumb Question: How these relation derived ?
Ans: Since PT makes angle
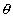 with x-axis, then
with x-axis, thentan
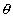 =
= 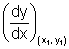
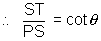
Subtangent = ST = PS cot
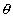
But PS = y1 & cot
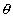 =
= 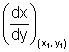 [see in fig.]
[see in fig.]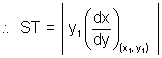
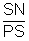 = cot(90 -
= cot(90 - 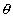 )
)  PS tan
PS tan
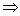 Subnormal = SN =
Subnormal = SN = 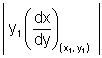
Length of tangent = PT =
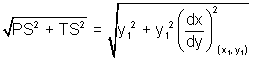
Length normal = PN =
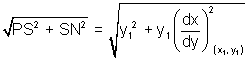
Illustration: Show that curve y = bex/a. subnormal varies as square of ordinate ?
Ans:
[Dumb Question: What is ordinate ?
Ans: y-axis component is c/d ordi i.e. in P(x1, y1)y1 is ordinate of point P.
y = bex/a ............................................... (i)
differentiating curve y = bex/a w.r.t. x.

& Let P(x1, y1) lie on curve
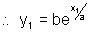
Length of subnormal =
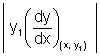
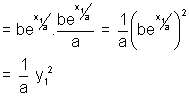
So, subnormal varies as square of ordinate.