Atomic Structure - 5
Shape of p-orbital:
Shape of p-orbital is dumb bell shape.
Note: No. of spherical/radial nodes in any orbital = n - 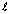 -1
-1
No. of planar nodes in any orbital = 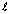
In s-orbital, spherical nodes & in p, d & f orbitals planar nodes.
 = a(z - b) = a(z - b) |
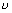
 frequency z
frequency z 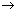 nuclear charge (atomic no.)
nuclear charge (atomic no.)Illustration: If straight line is at any angle 450 with intercept 1 on
 -axis. Calculate frequency
-axis. Calculate frequency 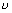 when atom c No. is 50.
when atom c No. is 50.Ans:
 = az - ab
= az - aby = mx + c
Slope = mx
 -axis intercept = - ab
-axis intercept = - abtan450 = 1 = a
- ab = 1
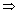 b = - 1
b = - 1 = z + 1
= z + 1 = (50 + 1)
= (50 + 1)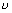 = (51)2 = 260 S-1
= (51)2 = 260 S-1Explanation of difference of energy in subshell of multielectron atoms:
In case of H-atom, only force of integration is force of attraction b/w -vely charged electron & +vely charged nucleus. But in multielectron atom, in addition to force of attraction b/w electrons & nucleus, there are forces of repulsion among electrons.
Atom is stable b/c net forces of attraction are greater than forces of repulsions.
Most imp. repulsive forces are on electrons of outer shell by electrons of inner shells. On other hand, attractive forces on electrons increase with
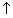 of nuclear charge (+ze). but these attractive forces on outershell electrons are greatly reduced by presence of inner shell electrons which produce a screening effect or shielding effect. b/w outer shell
of nuclear charge (+ze). but these attractive forces on outershell electrons are greatly reduced by presence of inner shell electrons which produce a screening effect or shielding effect. b/w outer shell..........
This is known as effective nuclear charge.
Note: (1) s-orbital, being spherical in shape, shields electron from nucleus more effectively than p-orbitals which in turn sheilds more effectively than d-orbitals.
(2 As effective nuclear charge depends upon actual nuclear charge. So, similar orbitalsof different atoms donot have same energy.
eg. E2s(H) < E2s(L) < E2s(Na)
Shpaes of orbitals:
s orbitals: Its shape is spherical.

p - orbitals:

d - orbitals:

Aufbau Principle: In ........... are filled in order of their increasing energies.
In neutral, isolated atom, lower value of (n +
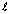 ) for orbital, lower is its energy.
) for orbital, lower is its energy.Note: If two different orbitals have same value of (n +
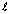 ), orbital with lower value of n has lower energy.
), orbital with lower value of n has lower energy.Hund's Rule of Max. Multiplicites:

Electron pairing in p, d & f orbitals cannot occur until each orbital of a given subshell contains one electron each or is singly occupied.
Illustration: Consider Nitrogen atom z = 7
