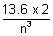Atomic Structure - 6
Rule for finding Group No.:
(i) If last shell contains 1 or 2 electrons, then group no. is 1 & 2 respectively.
(ii) If last shell contains more than 2 elctrons in last shell plus.
(iii) If electrons are present in (n n - 1)d orbital in addition to ns orbital, then gp. No. is equal to total no. of electrons present in (n - 1)d orbital & ns orbital.
Q.1. Two particles A & B are in motion. If wavelength associate with particle A is 5 x 10-8 m. Caclulate wavelength of B if momentum is half of A.
Ans: 
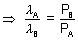 But PB =
But PB = 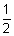 PA
PA
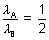
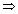
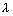 B = 2
B = 2 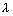 A
A
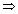
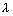 B = 10-7 m
B = 10-7 m
Q.2. Show that wavelength of a moving particle is related to its K.E. (E) as 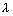 =
= 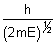
Ans: Acording de Broglie 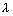 =
= 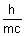
But 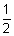 mv2 = E
mv2 = E 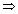 v =
v = 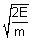
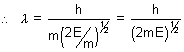
Q.3. A 25 watt bulb emits mouochromatic yellow light of wavelength of 0.57 µm. Calculate rate of emission of quanta/second.
Ans: Energy emitted/sec = 25 J/s
Energy of one photon (E) = h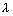 = h
= h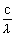
= 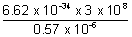 = 3.48 x 10-19 J
= 3.48 x 10-19 J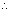 No. of photons enitted per sec =
No. of photons enitted per sec = 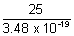
= 7.18 x 1019
Question: Calculate energy required to …….. from n = 2 orbit. What is longest wavelength of light in cm. can used ?
Ans: 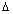 E =
E = 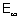 - E2 = 0 -
- E2 = 0 - 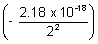 = 5.45 x 10-19 J/atom.
= 5.45 x 10-19 J/atom.
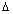 E = h
E = h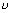 =
= 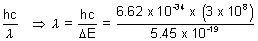
= 3.647 x 10-7
Q.5. An ion with mass no. 56 contains 30 mts +ve charge & 30.4% more neutrons than electrons. What is symbol of ion ?
Ans: Suppose no. of electrons in ion M3+ = x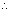 No. of neutrons = x +
No. of neutrons = x + 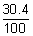 x = 1.304 x
x = 1.304 x
No. of electrons in neutral atom = x + 3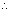 No. of protons = x + 3
No. of protons = x + 3
Mass no. = No. of photons + No. of neutrons
56 = x + 3 + 1.304 x
 x = 23
x = 23
No. of protons = 23 + 3 = 26
Symbol of will be 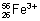
Q.6. In photon of wavelength 150p, strikes an atom & an bound electron ejected out with velocity 1.5 x 107 m/s. Calculate energy with which it bound to nucleus.
Ans: Energy of incident photon = 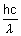
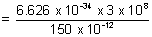 = 13.25 x 10-16 J
= 13.25 x 10-16 J
= 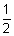 (9.11 x 10-31) x 1.5 x 107
(9.11 x 10-31) x 1.5 x 107
= 1.025 x 10-16 J
Energy with which electron was bound
= 13.25 x 1016 J - 1.025 x 10-16 J = 12.225 x 10-16 J
Q.7. If uncertainities in measurement of position and momentum of electron are equal in magnitude, what is uncertainity in measurement of velocity.
Ans: 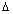 x x
x x 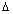 p =
p = 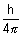
As 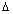 x =
x = 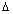 p
p 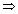
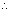 (
(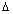 p)2 =
p)2 = 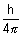
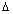 p =
p = 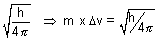
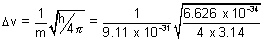
= 7.98 x 1012 m/s 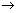 which is absurd.
which is absurd.
Q.8. A bulb emits light of wavelength 4500 A0. Bulb is rated as 150 watt & 8% of energy is emitted as light. How many photons are emitted by bulb per second.
Ans: Energy emitted/sec = 150 J/s Energy emitted as light =
Energy emitted as light = 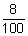 x 150 = 12 J = E
x 150 = 12 J = E
E = nh = nh
= nh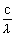
n = 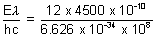
= 2.717 x 1019
Question: If H2 is exposed to radiation of wavelength 253 …, waht % of radiant energy will be converted into K.E. ?
Ans: Energy required to break H-H bond = 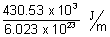
= 7.83 x 10-19 J
Energy of photon = 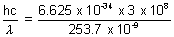
= 7.83 x 10-19 J
Energy left after dissociation = K.E. = (7.83 - 7.15) x 10-19
% of energy used in K.E. = 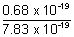 x 100 = 8.68 %
x 100 = 8.68 %
Q.10. Find velocity (m/s) of electron in Ist Bohr orbit of radius a0. Find be Broglie wavelength (in m). Find angular momentum of 2p orbital of H-atom.
Ans: For H & H-like atoms,
vn = 2.188 x 106 x 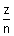 m/s
m/s
For H-atom, z =1 & for Ist orbit n = 1
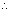 v = 2.188 x 106
v = 2.188 x 106
Debroglie wavelength, 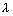 =
= 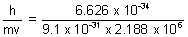
= 3.33 x 10-10 m
Orbital angular momentum = 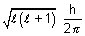
For 2p, 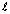 = 1,
= 1,
Orbital angular momentum = 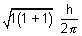
= 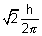
Q.1. A photon of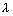 = 4 x
= 4 x  m strikes on metal surface, waork function of metal being 2.13 ev. Calculate (i) energy of photon (ev) (ii) K.E. of electron (iii) velocity of photoelectron.
m strikes on metal surface, waork function of metal being 2.13 ev. Calculate (i) energy of photon (ev) (ii) K.E. of electron (iii) velocity of photoelectron.
Ans: (i) Energy of photon = h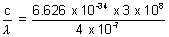
= 4.97 x 10-19 J
1ev = 1.6 x 10-19 J
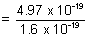 = 3.1 ev
= 3.1 ev
(ii) K.E. of electrons = h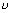 - h
- h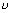 0 = 3.1 - 2.13 = 0.97 ev
0 = 3.1 - 2.13 = 0.97 ev
(iii) 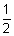 mv2 = 0.97 ev = 0.97 x 1.6 x 10-19
mv2 = 0.97 ev = 0.97 x 1.6 x 10-19
v2 = 0.341 x 1012 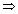 v = 5.84 x 105 m/s
v = 5.84 x 105 m/s
Q.2. In H-atom, energy of electron is nth orbit is given En = - 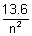 ev. Show that
ev. Show that
En + 1 - En = 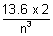 ev for large values of n.
ev for large values of n.
Ans: E(n + 1) - En = 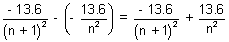
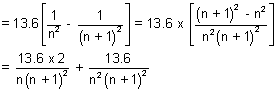
En + 1 - En 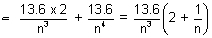
As n 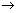
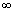 ,
, 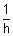
 0
0
En + 1 - En =