BOHR MODEL & X-RAYS - 3
few handy difinations:-
IONIZATION POTENTIAL:- The minimum energy needed to ionize an atom is called ionization energy, and the potential defference through which an electron should be accelerated to acquire this energy is called ionization potential. The ioniozation energy of hydrogen atom is ground state is 13.6 ev and ioniozation potentiation is 13.6 v.
BINDING ENERGY:- Binding enrgy of a system is defined as energy liberated when its constituents are brought from infinity to form the system. For hydrogen atom binding energy is same as its ionization energy.
EXCITATION ENERGY:- The energy required to take an atom from its ground state to an excited state is ncalled excitation energy of that excited state, and the potential.
ILLUSTRATION:- Find the longest and shortest wavelength in the Lyman Series for Lydrogen. In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum does each series lie ?
Solution:- The transition equation for Lyman Series is given by,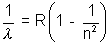 , n = 2, 3, ……………………
, n = 2, 3, ……………………
The longest wavelength is corresponding to n = 0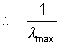 = 1.099 x 107(1 - 1/4) = 0.823 x 1s7
= 1.099 x 107(1 - 1/4) = 0.823 x 1s7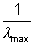 = 1.254 x 10- 7m = 1215
= 1.254 x 10- 7m = 1215![]()
The shortest wavelength corresponds to n = 
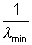 = 1.097 x 107(1 -
= 1.097 x 107(1 - 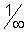 )
)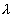 min = 0.911 x 10-7 m = 911
min = 0.911 x 10-7 m = 911 ![]()
AS can be seen both, the weavelength lie in ultraviolet (UV) region of electromagnetic spectrum.
X-RAYS
Electromagnetic radiations with wavelength from 0.1A0 to 100A0 falls into the category of X - rays, however the boundaries of this catygory are not sharp.
• The process of production of X-rays is reserve of photoelectric efffect. Here electromagnetic radiations are emitted by the bombordment of high speed thermionically emitted electrons on the metal surface.
X-rays produced are of two types:-
(a) CONTIMUOUS X-RAYS:- When electrons of vary high kinetic energy accelarates in an electric field then according to Maxwells theory, it radiates energy in the form of electromagnetics waves X-rays produced in this fashion are called continuous X-rays (also called Bremsstrahlung).
• Continuous X-rays produced at a given accelerating potential V very in wavelength, but none has wavelength shorten than a certain value 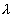 min.
min.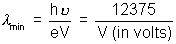 , V
, V ![]() potential aeron which electron is accelerated.
potential aeron which electron is accelerated.
Dumb Question:- What is the significance of this minimum wavelength of the X-Ray ?
Ans:- This minimum wavelength corresponds to the maximum energy of the X-ray produced. This condition occures when striking electron looses all its energy and this energy gets converted into X-rays. This for it
Energy of X-ray = total kinetic energy of electron = energy gained when accelerated across potential barrier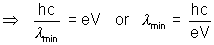
Note That the maximum wavelength  0 , this is the case when striking electron looses very small fraction of its energy.
0 , this is the case when striking electron looses very small fraction of its energy.
CHARACTERISTICS X-RAYS:- The sharp lines superimposed on the continuous spectrum are known as characteristic X-rays. because they are characteristic of the target material.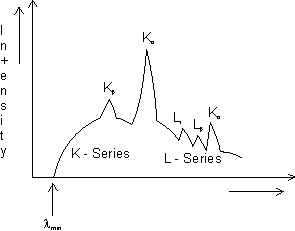 s
s
• Characteristic X-rays emission occures when a banbarding electron that collides with a target atom has sufficient energy to remove on inner shell electron from the atom.
• The vacancy created in the shell is filled when an electron from a higher level drops down into it. This transition is of a photon whose energy equals the difference in energy between the two levels.
Naming of characteristic X-rays:- Let the incoming electron dislodge an atomic electron from innermost shell - the K shell. If the vacancy is filled by an electron dropping from the next higher shell - the L shell emission is said to be of Kd series. If vacancy is filled by an electron dropping from M shell, 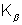 line is produced and Jo an.
line is produced and Jo an.
Dumb Question:- Why do 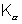 occur earlier than Kd in the plot ?
occur earlier than Kd in the plot ?
Ans:- 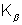 represents transition from higher shell then the kd line,
represents transition from higher shell then the kd line, 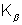 reperesents transition over larger energy range, thus would have lower wavelength as
reperesents transition over larger energy range, thus would have lower wavelength as 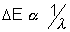 . thats why
. thats why 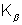 occurs earlier than Kd
occurs earlier than Kd