Carboxyllic-Acid-3
Acidic strength of carboxylic acid
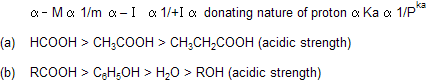
HCOOH is more acidic than benzoic acid due to +M effect of ring while inorganic acids like HCl, HI, HBr and HClO4 are strong acids than organic acids due to complete ionisation of these acids. Benzene sulphonic acid is highly acidic than carboxylic acid due to more number of intermediate resonanting structure of benzene sulphonate ion than acetate ion.
Acidic nature depends upon stability of anion
if G is electron withdrawing group it gives strength to acids while releasing nature of G decreases acidic nature. For example :
Due to +R effect or +I effect acidic nature decreases while – R and – I effect increases acidic power. Benzoic acid is weaker than formic acid due to +R effect of phenyl group in benzoic acid, but C6H5CH2COOH is stronger than CH3COOH because here phenyl group give – I effect
Some important acidic strength order are given below :
(i) FCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > BrCH2COOH > ICH2COOH > CH3COOH
(ii) CCl3COOH > Cl2CHCOOH > ClCH2COOH > HCOOH > CH3COOH
(iii) CH3CH2CH(Cl)COOH > CH3CH(Cl)CH2COOH > ClCH2CH2CH2COOH > CH3CH2CH2COOH
(iv) CH3COOH > CH3CH2COOH > (CH3)2CHCOOH > (CH3)3CCOOH
(v) NO2CH2COOH > NCCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > CH3COOH
(vi) OHCH2COOH > ClCH2COOH > CH3COOH
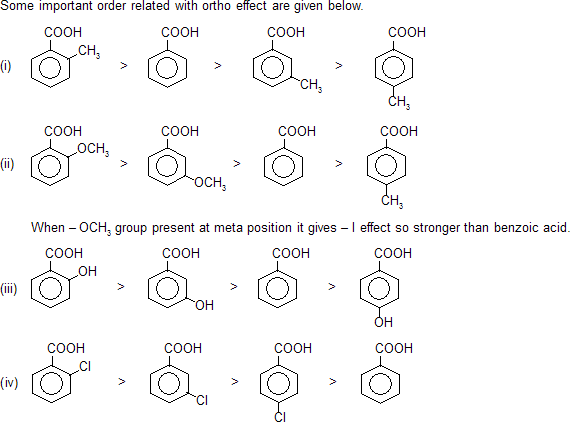
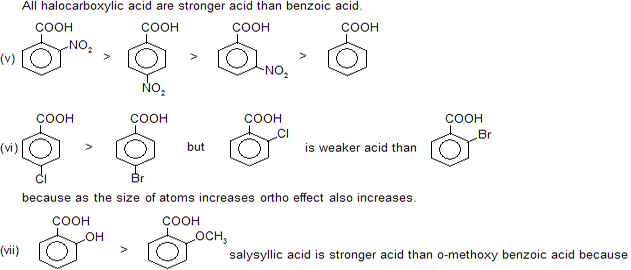
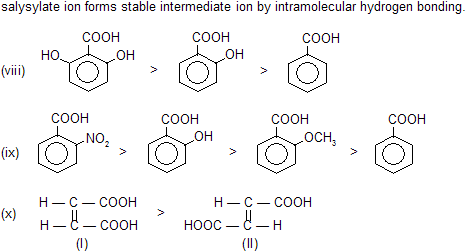
Any ortho substituted (electron releasing or electron attracting) group at benzoic acid always increase acidic nature. This is due to steric inhibition resonance by ortho group, known as ortho effect.