Chemical - Bonding-1
Hydrogen bond is formed when a slightly positive hydrogen atom, attached covalently to strong electronegative atom A (e.g., F, O or N) is held by a non-bonded electron pair of another atom B. The coordination number of hydrogen becomes two and it acts as a bridging atom between A and B.
![]()
Generally hydrogen bond is formed with only F, O and N atoms. Sometimes less electronegative atoms such as Cl, S etc., also take part in the formation of hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bond is denoted by dotted lines (...........). It can be defined as :
The attractive force that binds a hydrogen atom, which is already covalently attached with strongly electronegative atom of gain element is known as hydrogen bond. The bond energy of hydrogen bond is 3--10 kcal/mole.
Types of Hydrogen Bonding
Three types of hydrogen bonding exist :
(i) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding (ii) Intramolecular hydrogen bonding
(iii) ![]() -Hydrogen bonding
-Hydrogen bonding
(i) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding exists between two or more molecules of the same or different compounds.
(a) Homo-intermolecular hydrogen bonding. It is also termed as self-association. It refers to the association of two or more identical molecules e.g., association in alcohol, association in water, association in NH3, association in HF etc.
(b) Hetero-intermolecular hydrogen bonding. It refers to the association of two different species. One which donates the lone pair of electrons is called electron donor or hydrogen acceptor, while the other which donates proton is called proton donor. Example of hetero-intermolecular hydrogen bonding are as follows :
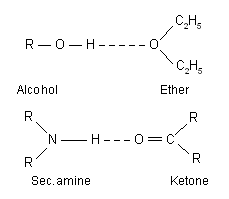
Due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding the molecules are associated together to form a cluster, which results in the increase in melting point and boiling point of the compound.