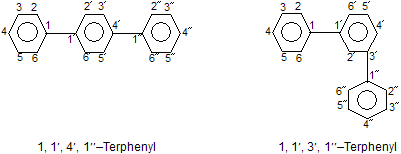common-names-geneva-system-9
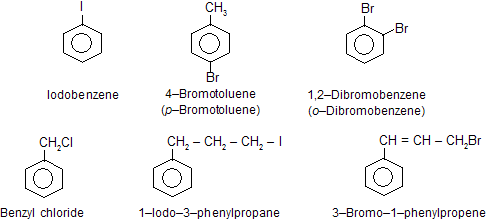
3. Nomenclature of halogen derivatives.
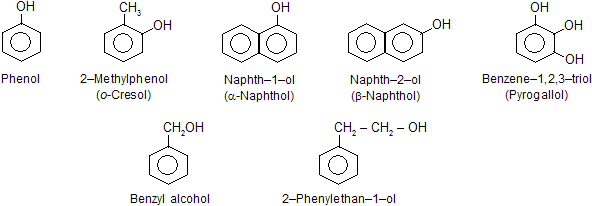
4. Nomenclature of hydroxy derivative.
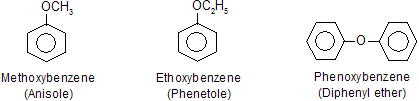
5. Nomenclature of aromatic ethers.
6. Nomenclature of aldehydes and ketones.
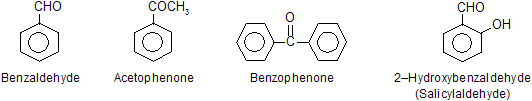
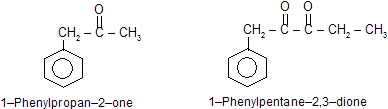
In above carbon chain is numbered from the end which gives lowest position to the > C = O group.
IUPAC nomenclature of two or more similar cyclic hydrocarbon units joined by a single bond
These systems are named by placing a suitable numerical prefix before the name of the repetitive hydrocarbon unit. The numerical prefixes used in this nomenclature are given below:
| Number of cyclic hydrocarbon units | Two | Three | Four | Five |
| Prefix | bi | ter | quater | quinque |
Starting from either end, the carbon atoms of each repetitive hydrocarbon unit are numbered with unprimed and primed Arabic numerals such as 1, 2, 3,................. 1', 2', 3',............ : 1", 2", 3",.............etc. The point of joining of the repetitive hydrocarbon units are indicated by placing the appropriate locants before the name. For example,
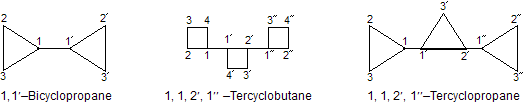
As an exception, unbranched assemblies consisting of benzene rings are named by using appropriate prefix under the name phenyl instead of benzene. For example,