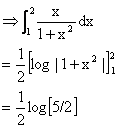differentiation-6
9) Find ![]()
Solution:
We have ![]()
Therefore by taking log on both sides we get,
logy = y log sinx.
Differentiating both sides w.r.t x we get,
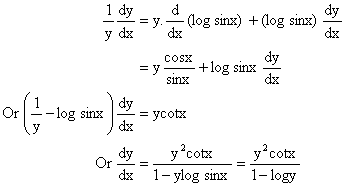
10) Is f(x) differentiable at x=0 if f(x) is defined as follow
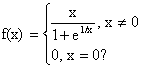
Solution:
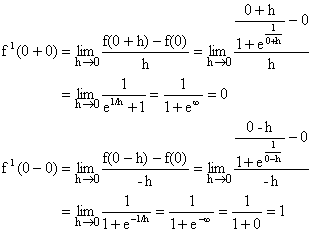
![]()
Here f(x) is not differentiable at x=0.
11) Determine the values of x for which the following function fails to be continuous or differentiable.
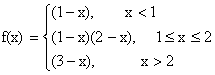
Justify your Answer.
Solution:
By given definition it is clear that the function f is continuous and differentiable at all points except possibility at x=1 and x=2.
Continuity at x=1,
L.H.L = ![]()
R.H.L = ![]()
Also f (1) = 0, Hence f(x) is continuous at x=1.
Now differentiability at x=1.
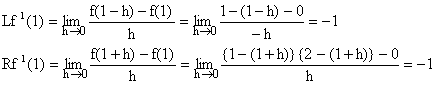
Since ![]() so we get f(x) is differentiable at x=1.
so we get f(x) is differentiable at x=1.
Continuity at x=2.
![]()
![]()
Since R.H.L ¹ L.H.L
Therefore f(x) is not continuous at x=2. As such f(x) can not be differentiable at x=2. Hence f(x) is continuous and differentiable at all points except at x=2.
12) If
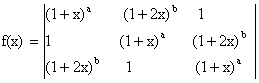 Then find a) Constant term b) Coefficient of x.
Then find a) Constant term b) Coefficient of x.
Solution:
Here 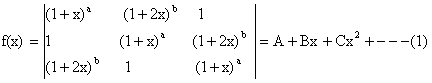
Putting x =0 we get
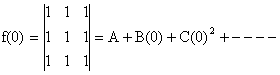
Þ A=0
Again Differentiating (1) w.r.t x we get,
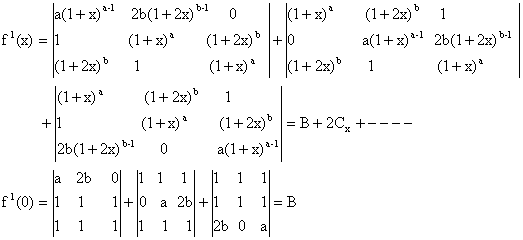
Therefore Coefficient of constant term = Coefficient of x = 0.
(MEDIUM TYPE)
1) Let f(x) be a real function not identically zero such that ![]() , nÎN and x, y are any real numbers and f1(0) ³ 0. Find the values of f (5) and f1(10).
, nÎN and x, y are any real numbers and f1(0) ³ 0. Find the values of f (5) and f1(10).
Solution:
Here ![]() ------ (1)
------ (1)
Putting x=0, y=0 we get f (0) = f (0) + {f (0)}2n+1.
\ f (0) = 0.
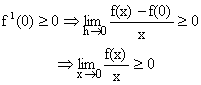
![]()
\ If x ³ 0, f(x) ³ 0 -------- (2)
Putting x = 0, y = 1 in (1)
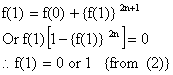
Putting y=1 in (1) for all real x,
f (x+1) = f(x) + {f (1)}2n+1------ (3)
\f (1) = 0 Þ f(x+1) = f(x)
Þ f (1) = f (2) = f (3) = ------ = 0
i.e. f(x) is identically zero.
\ f (1) ¹ 0 Hence f (1) =1.
So from (3) f(x+1) = f (x) +1 ---- (4)
\ f (5) = f (4) +1 = {f (3) + 1}+ 1
= {f (2) +1} +2
= {f (1) +1} +3
=f (1) +4
=1+4
=5
Also (4)Þ f(x) is a function whose value increases by 1.When variable x is increased by 1.
\f (x) = x \f1(x) = 1
\ f1(10) =1.
Dumb Question:
1) Why does the equation ![]() has the solution as f (1) = 0, 1? Some complex solution could also be possible.
has the solution as f (1) = 0, 1? Some complex solution could also be possible.
Ans: It is mentioned in the question that function f is real valued function, so the value of f (1) has to be real and cannot be complex.
2) If f be a function such that f (xy) = f (x). f (y), " yÎR and f (1+x) = 1+x (1+ g(x)). Where ![]() , find the value of
, find the value of ![]()
Solution:
We know,
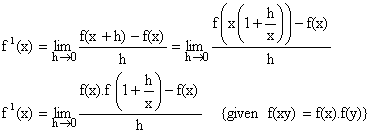
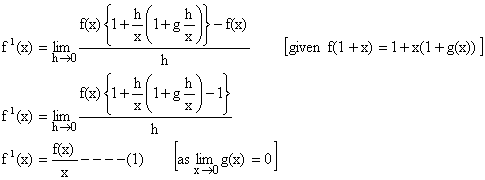
To find ![]()