Electric Capacitance And Capacitor - 1
Electric Capacitance And Capacitor
The capacitance of any conductor is its capacity to store charge. As the quantity of charge on conductor is increased its potential also increases. Beyond a limit even if a small additional charge is given then it starts leaking.
Hence Q µ V or Q = CV.
Where C is called capacitance of the conductor. It depends upon geometrical shape and size of the conductor.
If V = 1 volt, then Q = C, hence capacitance of any conductor will be numerically equivalent to that charge which makes its potential equal to 1 volt.
Unit of capacitance is ‘Farad’:
1 Farad = 1 coulomb/1 volt.
= coulomb/ (joule/coulomb).
= coulomb2/joule.
= (ampere x second) 2 / (
3) Dimensions of capacitance:
![]()
In practice 1 Farad is very large capacity therefore its small units are as following:
1) 1 micro-farad = 10-6 farad = 1mf.
2) 1 nano-farad = 10-9 farad = 1hf.
3) 1 pico-farad or micro-micro farad = 10-12 farad = 1rf = 1mmf.
4)
Capacitance of spherical conductor:
For a spherical conductor of radius R,
Potential is ![]()
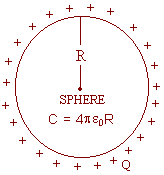
Fig (1)
1) ![]() .
.
2) \ C µ R.
3) C (capacitance) does not depend upon the charge given.
5) Energy stored in a charged conductor:
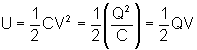
6) Redistribution of charge:
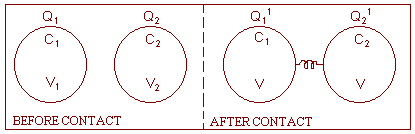
Fig (2)