Electric Current - 7
Question :-
Electrical circuit is shown in figure. Calculate the potential difference across the resistor of 400 ohms as will be measured by the voltmeter V of resistance 400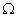 either by applying Kirchoff’s laws or otherwise.
either by applying Kirchoff’s laws or otherwise.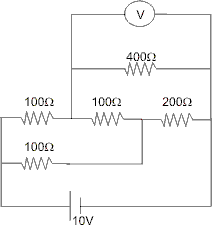
Ans :- This circuit is equivalent to :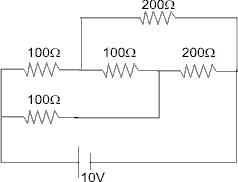
Which in turn is equivalent to :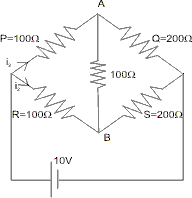
As, it is a balance Wheat Stone’s Bridge as .
. of 100
of 100 between A and B can be ignored.
between A and B can be ignored.
The voltage will read the potential difference across Q.
First we find that i1 = i2 = 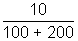
 .
. Potential difference across resistance Q = Q X i1
Potential difference across resistance Q = Q X i1 .
.
Therefore, Voltmeter will read 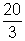 V.
V.
Question :-
Charging and 100 V after charging. When charging below the current was 5A. What is the current at the end of the charging if the internal resistance is equal and constant to 8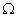 in the whole process.
in the whole process.
Ans :- The voltage supplied is constant for both times and equal V given by -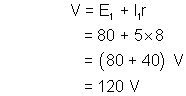
Let the current finaly (at the end of charging br I)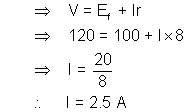
H -1: A conductors has a temperature independent resistance R and its total heat capacity is C. At t = 0 it is connect to d.c. voltage source V. Find T(t) assuing power dissipated into surrounding space to very as q = k(T - T0) where k is constant, T0 is surrounding temperature (and equals conductor’s initial temperature) ?
Ans :- Energy supplied by source/unit time = energy lost in environment/unit time + energy used in raising temp/unit time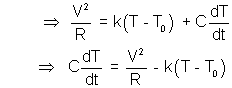
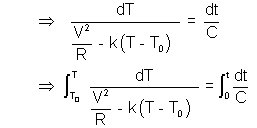
On solving : 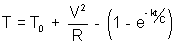 .
.
Dumb Question - 11. How we get the initial equation of the above question ?
Ans Initial equation states :
Energy supplied by source/unit time = energy lost to surroundings/unit time + energy used in raising temp/unit time
On close observation one finds that it is just the Law of Conservation of Energy.
M - 2. What amount of heat will be generated in a resistance R due to a charge q passing through it if the current in the coil :
(a) Decreases down to zero uniformly during a time internal to ?
Ans (a) Drawing corresponding i - t graph :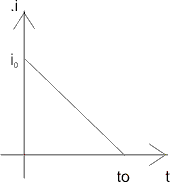
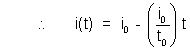
i0 can be found by the information that charge q = area it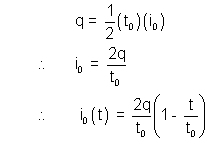
At any time t assume a small increament in time dt such that dt 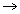 0.
0.
dH = Heat produced in this time interval = i2Rdt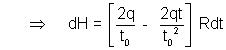
Total Heat produced = 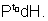 .
.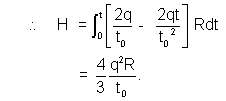
Dumb Question - 18. How charge = Area under it graph ?
Ans :- We know that Current = I = 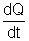
Thus, dQ = I dt
Integrating both sides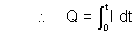 [Assuming at t = 0, Q = 0].
[Assuming at t = 0, Q = 0].
Now, 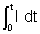 is nothing but area under the It graph.
is nothing but area under the It graph.
H - 3. A voltmeter of resistance R1 and an ammeter of resistance R2 are connected in series across a negligible resistance battery. When a resistance R is connected in parallel to voltmeter, ammeter increases its reading to three times and voltmeter’s reading reduces by one third. Find R1 and R2 in terms of R ?
Ans :- Case I :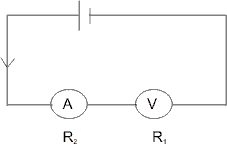
In this case E = I(R1 + R2).
Case II :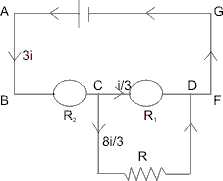
Now, as ammeter reads 3 times so, net current 3i is drawn from the battery.
Current in voltmeter resources to Remaining
Remaining 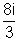 passes through R.
passes through R.
VC - VD = 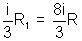
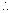 R1 = 8R.
R1 = 8R.
Applying Kirchoff’s Voltage Rule in ABFGA :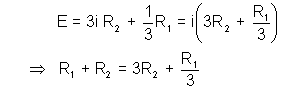
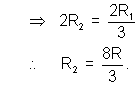
- Average Current
- Instantaneous Current
- Current Density
- Drift Velocity
- Ohm’s law
- Resistivity
- Kirchoff’s Laws
- Internal Resistance of a battery
- Grouping of Resistance :-
(a) Serial
(b) Parallel - Heating Effects of Current
- Joule effect
- Maximum Power Transfer Theorem
- Grouping of Cells
- Galvanometer
- Ammeter
- Voltmeter
- Wheat Stone’s Bridge
- Potentiometer