Electro - Chemistry-1
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
Chemistry: Physical Chemistry Chapter
In mid, 17808 anatomist Luigi Galvani (Italy) was studying effects of atm. electric discharge. One day, in his garden, he fastened bross hooks b/w spinal cord of dissected frof and iron railing. He should that frog's leg began twitching wildly. He interpreted as animal electricity.In 1777, Alessandro volta repeated Galvani's famous experiments with decapitated frogs ole interpreted that twitches were due flowing of current b/w two dissimilar metals connected moist flesh of frog's leg.
In 1801 volta awarded by Napolean a gold his discovery.
Faraday achieved scientific prominence of his own for Ist law of Electrochemistry, developed in 1834.
Electrochemistry: It is branch of chemistry which deals with relationship b/w clectrical energy & chemical changes taking place in redox reactions.
Electrolysis: Process of decomposition of an electrolyte by passage of electricity through its aq. solution or molten state.
Mechanism of electrolysis: Electro dissociates producing +ve & -vely charged ions. On passing electric current, positively charged ions move towards cathode & hence c/d cations & lose their respective charge. Similarly -ve ions moves towards Anode c/d anions. So, oxidation occursat anode while reduction takes place at cathode.
Electrolysis water: Initialy, ammeter does not show any deflection. b/c water is bad conductor of elecricity.
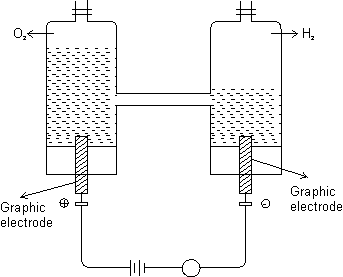
WHen few drops od oil. H2SO4 are added to water, ammeter shows a deflection & electrolysis begins. As a result electrolysis, oxygen isproduced at anode & H2 at cathode.
Vol. of H2 evolved is double that of oxygen.
H2O(l)
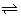 H+(aq.) + on-(aq.)
H+(aq.) + on-(aq.)H2SO4(aq.)
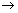 2H+(as) + SO42-(aq.)
2H+(as) + SO42-(aq.)When electric current is passed through it, H+ ions moves towards cathode & on- & SO42- ions move towards anode.
Since discharge potential of on- ions is much lower than that of SO42- ions. So, SO42- ions remains in sol.
At Cathode:
H+(aq) + e-
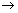 H. (primary change)
H. (primary change)H. + H.
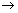 H2(I) (Secondary Change)
H2(I) (Secondary Change)At Anode:
on-(aq.) - e-
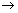 OH
OH4OH
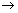 2H2O + O2
2H2O + O2Overall reaction:
4H+(aq.) + 4on-(aq.)
 2H2(aq) + 2H2O(l) + O2(I)
2H2(aq) + 2H2O(l) + O2(I)Faraday's Ist law of electrolysis: Mass of any substance deposited or liberated at any electrode is directly proportional to quantity of electricity passed.
If Wg of substance deposited on passing Q coulombs of electricity. then,
W
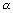
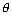
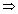 W = z
W = z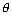 z
z 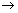 electrochemical equivalent
electrochemical equivalentIf current of camperes is passed for t seconds, then
Q = c x t
W = z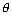 = zct = zct |
Faraday's IInd law: When same quantity of electricity is passed through solutions of different electrolytes connected in series, weights of substances produced at electrodes aredirectly proportional to their equivalent weights.
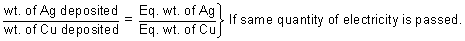
Cu2+ + 2e-
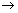 Cu Al3+ + 3e-
Cu Al3+ + 3e- 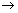 Al
Altwo moles of electrons produce one mol of Cu, 3 moles of electron will produce 1 mol. of Al.
Total charge of 1 mol of electron = 1.6023 x 10-19 x 6.022 x 1023
= 96490 coulombs = 1 Faraday.
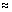 96500 Cmol-1
96500 Cmol-1Note: If n electrons are involved in electrode rxn, passage of n. faradys of electricity will liberate 1 mol of substance. - 1 faraday deposits 1 gm equivalent of subatance.
z =
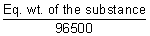
Eq. wt = 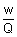 x 96500 x 96500 |
| Electrical energy in jouls = V(volts) x Q(coulombs) |
Transport No.: Fraction of current carried by an ion is c/d its transport No. As current by an ion depends upon its speed.
Transpost no. of cation, nc =
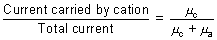
Transport no. of anion, na =
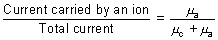
Illustration: Silver is electro-deposited on a metallic vessel of surface area 800 cm2 by passing a current 0.2 ampere for 3 hrs. Calculate thickness of silver deposited.
density of silver = 10.47 g/sec & Atomic mass = 107.92 amu.
Ans: Quantity of electricity passed = 0.2 x 3 x 60 x 60 = 2160 c
96500 deposit Ag = 1.07.92 g
2160 will deposit Ag =
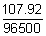 x 2160 = 2.4156 g
x 2160 = 2.4156 gVolume deposited =
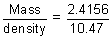 = 0.2307 cc
= 0.2307 ccThickness deposited =
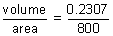 = 2.88 x 10-4 cm.
= 2.88 x 10-4 cm.