Electro - Chemistry-3
Conductance Behaviour of weak electrolyte:
As weak electrolyte dissociates to a much lesser extent than strong electrolyte. For weak electrolyte, there is a very large increase in conductance with dilution. B/C conc. of electrolyte & no. of ions in sol.
& no. of ions in sol.  . So, conductance
. So, conductance  .
.
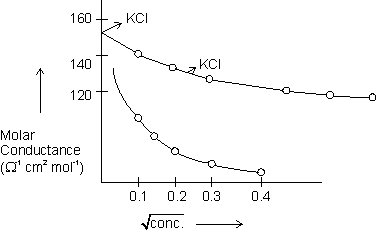
Illustration: Conductivity of NaCl at 298 K at different conc. is given.
Conc. (m) 0.001 0.01 0.02
10-2 x K (Sm-1 1.237 11.85 23.15
Calculate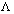 for all conc. & find
for all conc. & find 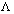 0 & slope.
0 & slope.
Ans: 1 S cm-2 = 100 S m-1
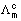 =
= 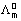 - A
- A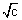 ................................... (i)
................................... (i)
Slope = - A
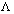 m =
m = 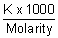 (S cm2 mol-1)
(S cm2 mol-1)
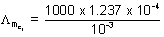 = 123.7 ............... (ii)
= 123.7 ............... (ii)
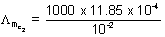 = 118.5 .............. (iii)
= 118.5 .............. (iii)
123.7 =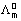 - A(0.0316) ...................... (iv)
- A(0.0316) ...................... (iv)
118.5 =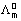 - A(0.1) ........................... (v)
- A(0.1) ........................... (v)
On solving we get
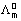 = 124 S cm2mol-1
= 124 S cm2mol-1
118.5 = 124 - A(0.1)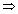 A = 55
A = 55 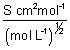
Kolilrausch law: Limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte (molar conductivity at infinite diution) is sum of limiting ionic conductivities of cation & anion each multiplied with no. of ions present in one formula unit of electrolyte.
eg.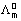 for AxBy =
for AxBy = 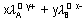
or
Eq. conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is sum of two values one depending upon cation & other upon anion.
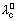 &
& 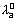
 Ionic conductivities at infinite dilution.
Ionic conductivities at infinite dilution.
Applications:
(1) Calculation of Molar Conductivity at infinite dilution (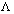 0) for weak electrolytes:
0) for weak electrolytes:
Illustration: Calculate molar conductance at infinite dilution for CH3COOH.
 (HCl) = 425
(HCl) = 425  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1  (NaCl) = 188
(NaCl) = 188  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1
 (CH3COONa) = 96
(CH3COONa) = 96  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1
Ans: (CH3COOH) =
(CH3COOH) =  (CH3COO-) +
(CH3COO-) +  (H+)
(H+)  Required.
Required.
 (HCl) =
(HCl) =  (H+) +
(H+) +  (Cl) ....................................... (i)
(Cl) ....................................... (i)
 (NaCl) =
(NaCl) =  (Na+) +
(Na+) +  (Cl) .................................... (ii)
(Cl) .................................... (ii)
 (CH3COONa) =
(CH3COONa) =  (CH3COO-) +
(CH3COO-) +  (Na+) .................. (iii)
(Na+) .................. (iii)
By (i) + (iii) - (ii), we get required
 (CH3COO-) +
(CH3COO-) +  (H+) = 425 + 96 - 188
(H+) = 425 + 96 - 188
= 333 -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1
(2) Calculation of deg. of dissociation:
 in molar conductivity with dilution is due to increase in dissociation of electrolyte.
in molar conductivity with dilution is due to increase in dissociation of electrolyte.
Deg. of dissociction (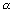 ) =
) = 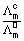
(3) Calculation of dissociation constant:
K can be calculated if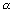 is known.
is known.
Illustration: Conductivity of 0.001 M CH3COOH is 4.95 x 10-5 S cm-1. Calculate its dissociation constant. Gijven for acetic acid,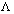 0 is 390.5 S cm2 mol-1.
0 is 390.5 S cm2 mol-1.
Ans: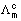 =
= 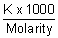 =
= 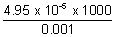 = 49.5 S cm2 mol-1
= 49.5 S cm2 mol-1
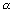 =
= 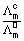
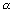 =
= 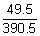 = 0.127
= 0.127
K =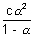 =
= 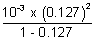 = 1.85 x 10-5
= 1.85 x 10-5
(4) Calculation of solubility of sparingly soluble salt:
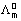 =
= 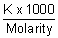 =
= 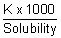
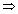 Solubility =
Solubility = 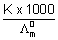
Illustration: Conductivity of solurated sol. of Agcl at 288 K is found to be 1.382 x 10-6 -1 cm-1. Find its solubility
-1 cm-1. Find its solubility
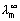 (Ag+) = 61.9
(Ag+) = 61.9  -1 cm2 mol-1 &
-1 cm2 mol-1 & 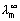 (Cl-) = 76.3
(Cl-) = 76.3  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1
Ans: (AgCl) =
(AgCl) = 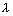 0Ag+ +
0Ag+ + 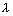 0Cl- = 61.9 + 76.3 = 138.2
0Cl- = 61.9 + 76.3 = 138.2  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1
Solubility =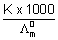 =
= 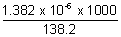
= 10-5 mol L-1 = 10-5 x 143.5 g/L
= 1.435 x 10-3 g/L
(5) Calculation of Ionic product of H2O:
Ionic conductance of H+ & on- at infinite dil.
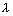 0n+ = 349.8
0n+ = 349.8  -1 cm2 &
-1 cm2 & 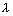 0OH- = 198.5
0OH- = 198.5  -1 cm2
-1 cm2
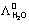 =
= 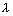 0H+ +
0H+ + 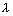 0OH-
0OH-
= 349.8 + 198.5 = 548.7 -1 cm2
-1 cm2
Sp. conductance of pure water at 298 K is found to be
K = 5.54 x 10-8 -1 cm-1
-1 cm-1
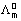 = K x
= K x 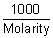
Molarity i.e. [H-1] or [on-] =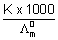
=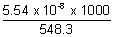 = 1.01 x 10-7 mol/L
= 1.01 x 10-7 mol/L
 Kw = [H-1] [on-]
Kw = [H-1] [on-]
= 1.01 x 10-7 x 1.01 x 10-7 = 1.02 x 10-14 mol/L
As weak electrolyte dissociates to a much lesser extent than strong electrolyte. For weak electrolyte, there is a very large increase in conductance with dilution. B/C conc. of electrolyte
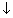 & no. of ions in sol.
& no. of ions in sol. 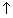 . So, conductance
. So, conductance 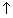 .
.
Illustration: Conductivity of NaCl at 298 K at different conc. is given.
Conc. (m) 0.001 0.01 0.02
10-2 x K (Sm-1 1.237 11.85 23.15
Calculate
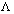 for all conc. & find
for all conc. & find 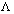 0 & slope.
0 & slope.Ans: 1 S cm-2 = 100 S m-1
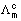 =
= 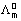 - A
- A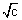 ................................... (i)
................................... (i)Slope = - A
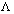 m =
m = 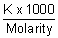 (S cm2 mol-1)
(S cm2 mol-1)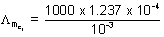 = 123.7 ............... (ii)
= 123.7 ............... (ii)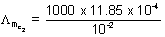 = 118.5 .............. (iii)
= 118.5 .............. (iii)123.7 =
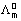 - A(0.0316) ...................... (iv)
- A(0.0316) ...................... (iv)118.5 =
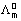 - A(0.1) ........................... (v)
- A(0.1) ........................... (v)On solving we get
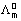 = 124 S cm2mol-1
= 124 S cm2mol-1118.5 = 124 - A(0.1)
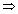 A = 55
A = 55 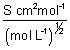
Kolilrausch law: Limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte (molar conductivity at infinite diution) is sum of limiting ionic conductivities of cation & anion each multiplied with no. of ions present in one formula unit of electrolyte.
eg.
 for AxBy =
for AxBy = 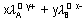
or
Eq. conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is sum of two values one depending upon cation & other upon anion.
 eq = eq = 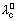 + + 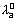 |
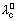 &
& 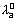
 Ionic conductivities at infinite dilution.
Ionic conductivities at infinite dilution.Applications:
(1) Calculation of Molar Conductivity at infinite dilution (
 0) for weak electrolytes:
0) for weak electrolytes:Illustration: Calculate molar conductance at infinite dilution for CH3COOH.
 (HCl) = 425
(HCl) = 425  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1  (NaCl) = 188
(NaCl) = 188  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1 (CH3COONa) = 96
(CH3COONa) = 96  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1Ans:
 (CH3COOH) =
(CH3COOH) =  (CH3COO-) +
(CH3COO-) +  (H+)
(H+)  Required.
Required. (HCl) =
(HCl) =  (H+) +
(H+) +  (Cl) ....................................... (i)
(Cl) ....................................... (i) (NaCl) =
(NaCl) =  (Na+) +
(Na+) +  (Cl) .................................... (ii)
(Cl) .................................... (ii) (CH3COONa) =
(CH3COONa) =  (CH3COO-) +
(CH3COO-) +  (Na+) .................. (iii)
(Na+) .................. (iii)By (i) + (iii) - (ii), we get required
 (CH3COO-) +
(CH3COO-) +  (H+) = 425 + 96 - 188
(H+) = 425 + 96 - 188= 333
 -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1(2) Calculation of deg. of dissociation:
 in molar conductivity with dilution is due to increase in dissociation of electrolyte.
in molar conductivity with dilution is due to increase in dissociation of electrolyte.Deg. of dissociction (
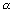 ) =
) = 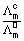
(3) Calculation of dissociation constant:
Kc = 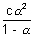 |
K can be calculated if
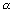 is known.
is known.Illustration: Conductivity of 0.001 M CH3COOH is 4.95 x 10-5 S cm-1. Calculate its dissociation constant. Gijven for acetic acid,
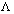 0 is 390.5 S cm2 mol-1.
0 is 390.5 S cm2 mol-1.Ans:
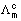 =
= 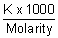 =
= 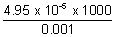 = 49.5 S cm2 mol-1
= 49.5 S cm2 mol-1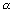 =
= 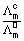
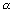 =
= 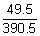 = 0.127
= 0.127K =
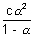 =
= 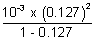 = 1.85 x 10-5
= 1.85 x 10-5(4) Calculation of solubility of sparingly soluble salt:
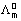 =
= 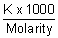 =
= 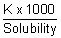
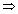 Solubility =
Solubility = 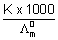
Illustration: Conductivity of solurated sol. of Agcl at 288 K is found to be 1.382 x 10-6
 -1 cm-1. Find its solubility
-1 cm-1. Find its solubility (Ag+) = 61.9
(Ag+) = 61.9  -1 cm2 mol-1 &
-1 cm2 mol-1 & 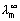 (Cl-) = 76.3
(Cl-) = 76.3  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1Ans:
 (AgCl) =
(AgCl) = 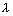 0Ag+ +
0Ag+ + 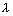 0Cl- = 61.9 + 76.3 = 138.2
0Cl- = 61.9 + 76.3 = 138.2  -1 cm2 mol-1
-1 cm2 mol-1Solubility =
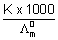 =
= 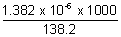
= 10-5 mol L-1 = 10-5 x 143.5 g/L
= 1.435 x 10-3 g/L
(5) Calculation of Ionic product of H2O:
Ionic conductance of H+ & on- at infinite dil.
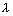 0n+ = 349.8
0n+ = 349.8  -1 cm2 &
-1 cm2 & 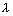 0OH- = 198.5
0OH- = 198.5  -1 cm2
-1 cm2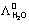 =
= 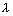 0H+ +
0H+ + 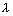 0OH-
0OH-= 349.8 + 198.5 = 548.7
 -1 cm2
-1 cm2Sp. conductance of pure water at 298 K is found to be
K = 5.54 x 10-8
 -1 cm-1
-1 cm-1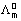 = K x
= K x 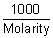
Molarity i.e. [H-1] or [on-] =
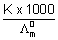
=
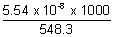 = 1.01 x 10-7 mol/L
= 1.01 x 10-7 mol/L Kw = [H-1] [on-]
Kw = [H-1] [on-]= 1.01 x 10-7 x 1.01 x 10-7 = 1.02 x 10-14 mol/L