Q.10. Standard reduction potential for Cu
2+/Cu is +0.34 v. Calculate reduction potential at P
H = 14
K
sp of Cu(OH)
2 is 1.0 x 10
-19Ans: For Cu(OH)
2, K
sp = [Cu
2+][on
-]
2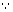
P
H = 14 So, [H
+) = 10
-14 K
w = [H
+)[OH
-)
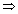
[OH
-) =
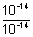
= 1
So, [Cu
2+] =
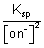
= 1.0 x 10
-19 = 1 x 10
-19 E
cell = E
0cell +
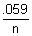
log
10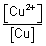
= 0.34 +
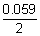
log
10[Cu
2+]
= 0.34 +
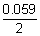
log
10[1 x 10
-19]
E
cell = - 0.2205 v at P
H = 14
Medium Type
Q.1. In a fuel cell H
2 & O
2 react to produceelectricity. In process H
2 gas is oxidized at anode& O
2 at cathode. If 67.26 of H
2 atSTP reacts in 15 min. What is avg. current produced ? If entire current is used for electrodeposition of Cu from Cu
2+, how many gm of Cu are deposited ?
Cathode: O
2 + 2H
2O + 4e
- 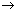
4OH
- Anode: H
2 + 2OH
- + 4e
- 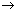
2H
2O + 2e
-Ans: Moles of H
2 reacting =
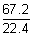
= 3
Eq. of H
2 used = Moles x n-factor
= 3 x 2 = 6
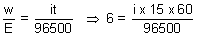
i = 643.33 A
Also, Eq. of H
2 = Eq. of Cu formed
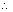
w
Cu = 6 x
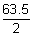
= 190.5 g
wt. of Cu deposited = 190.5 g
Q.2. 19 g fused SnCl
2 was electrolysed using inert electrodes. 0.119 g Sn was deposited at cathode. If nothing was given out during electrolysis, calculate ratio of wt. of SnCl
2 & SnCl
2 in fused state after electrolysis (at. et. Sn = 119).
Ans: electrolysis SnCl
2 yieldes:
Anode: 2Cl
- 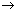
Cl
2 + 2e
- Cathode: Sn
2+ + 2e
- 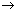
Sn
Further Cl
2 formed at anode reacts with SnCl
2 to give SnCl
4 SnCl
2 + Cl
2 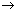
SnCl
4Eq. of SnCl
2 lost during electrolysis = Eq. of Cl
2 formed during electrolysis = Eq. of Sn formed.
Eq. of Cl
2 formed =
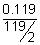
= 2 x 10
-3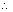
Eq. of SnCl
4 formed = 2 x 10
-3 (
whole Cl
2 react to from SnCl
4)
Now, total loss in Eq. of SnCl
4 during complete course
= Eq. of SnCl
2 lost during electrolysis + Eq. of SnCl
2 lost during reaction with Cl
2 = 2 x 10
-3 + 2 x 10
-3 = 4 x 10
-3Initial eq. of SnCl
2 left in sol. = 2 x 10
-1 - 4 x 10
-3 = 0.196
Eq. of SnCl
4 formed = 2 x 10
-3 = 0.002
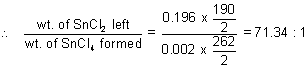
Q.3. Calculate emf of given cell rxn. and Pb(s) + Hg
2So
4 
PbSO
4(s) + 2H
g(l)
Given
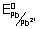
= 0.126
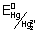
= - 0.789 v
K
SP of PbSO
4 = 2.43 x 10
-8 K
SP of Hg
2SO
4 = 1.46 x 10
-6.
Ans: Oxidation potential = - REduction Potential
Anode: Pb
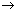
Pb
2+ + 2e
2e- Cathode: Hg
22+ + 2e
- 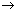
HG
2 E
cell = E
0cell -
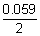
log
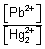
= (
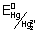
-
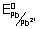
) -
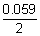
log
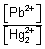
= 0.789 - (- 0.126) -
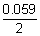
log
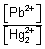
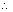
K
SP = [Pb
2+][SO
42-] = [Pb
2+]
2 [
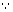
[Pb
2+] = [SO
42-]]
[Pb
2+] =
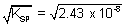
Similarly,
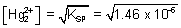
E
cell = 0.789 + 0.126 -
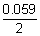
log
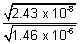
= 0.941
Q.4. Two weak acid sol. HA
1 & HA
2 each with same conc. & having P
Ka values 3 & 5 are placed in contact with Hydrogen electrode (1atm, 25
0c) and are interconnected through salt bridge. Find emf of cell.
Ans: Cell is
Pt H
2(1 atm)|HA
2||HA
1|(H
2)(1 atm) P
tAt L.H.S.,
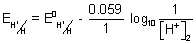
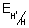
= 0 - 0.059 (P
H)
2At R.H.S.,
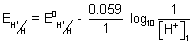
= - 0.059 (P
H)
1For acid HA
1,
HA
1 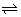
H
+ + A
1- [H
+) = c
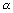
=
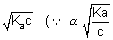
if
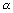
is small)
(P
H)
1 =
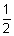
PK
a -
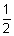
log
10c
Similarly,
(P
H)
2 =
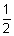
PK
a -
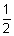
logc
E
cell = - 0.059(P
H)
1 + 0.059(P
H)
2 = 0.059[
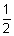
P
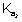
-
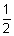
P
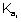
] =
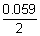
[5 - 3]
= 0.059 v
Q.5. REduction potential diagram for Cu in acid solution is:
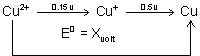
Calculate value of X.
Ans: Given, Cu
2+ + e
- 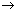
Cu
+;
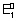
= 0.15 v ;
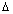
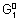
........................... (i)
Cu
+ + e
- 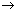
Cu
+ ,
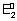
= 0.5 v ;
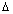
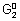
........................... (ii)
Cu
2+ + 2e
- 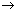
Cu ;
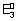
= ? ;
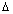
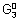
........................... (iii)
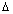
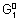
= - n

F = - 1 x 0.15 F = - 0.15 F
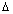
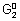
= -n
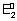
F = - 1 x 0.5 x F = - 0.5 F
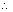
Adding
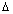
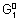
+
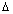
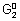
=
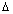
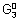
- 0.15 F + (- 0.5 F) =
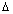
= - 0.65 F
- n
F = - 0.65 F
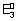
=
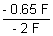
= 0.325 volt.
X = 0.325 Volt