HARD TYPE
Q.1. Standard potential of following cell is 0.23V at 15
0C and 0.21V at 35
0C
Pt H
2(g)|HCl(ag.)|AgCl(s)|Ag(s)
(i) Calculate

n
0 &

S
0 for cell rxn . by assuming that these quantities remains unchanged in range 15
0 & 35
0C.
(ii) Calculate solubility of AgCl in H
2O at 25
0C. Given, standard reduction potential of Ag
+(ag.)/Ag(s) couple is 0.8v at 25
0C.
Ans: Pt H
2(g)|HCl(ag.)|AgCl(s)|Ag(s)
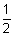
H
2 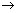
H
+ + e
- (Anode)
AgCl + e
- 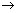
Ag + Cl
- (Cathode)

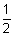
H
2 + AgCl
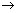
n
+ + Ag + Cl
- -

G
0 = nE
0F = 1 x 0.23 x 96500 = 2219 SJ (at 25
0 c)
-

G
0 = nE
0F = 1 x 0.21 x 96500 = 2026 SJ (at 35
0 c)

G
0 =

H
0 - T

S
0 - 22195 =

H
0 - 298 x

S
0 ................................. (i)
- 20265 =

n
0 - 308 x

S
0 ................................. (ii)
On solving

S
0 = -96.5 J &

H
0 = 49.987 KJ
(ii) Ag
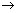
Ag
+ + e
- E
0OP = - 0.8 V
Agcl + e
- 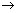
Ag + Cl
- 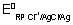
=
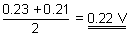

AgCl
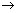
Ag
+ + Cl
- 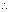
E
cell =
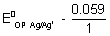
log[AG
+] +
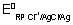
+
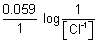
At eqm,
E
cell = 0
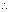
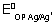
+
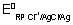
=
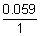
log[Ag
+][Cl
-] = 0.059 logK
SP AgCl - 0.8 + 0.22 = 0.059 logK
SP K
SP = 1.47 x 10
-10 Solubility of AgCl =
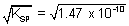
= 1.21 x 10
-5 mol/L
Q.2. Overall formation constant for reaction of 6 mole of CN
- with cobalt (II) is 1 x 10
19. Calculate formation constant for rxn. of 6 mole of CN
- with cobalt (III). Given that
CO
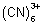
+ e
- 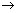
CO
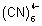
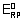
= - 0.83 V
CO
3+ + e
- 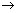
CO
2+ 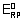
= 1.82 V
Ans: CO
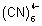
CO
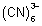
+ e
- 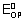
= 0.83V
CO
3+ + e
- 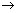
CO
2+ 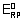
= 1.82 V

CO
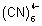
+ CO
3+ 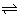
CO
2+ + CO
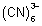
E
cell = E
0cell -
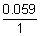
log
10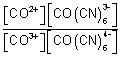
Also, 6CN
- + CO
2+ 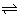
CO
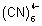
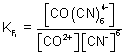
& 6CN
- + CO
3+ 
CO
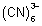
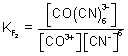
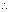
E
cell = E
0cell +
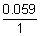
log
10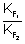
At eqm. E
cell = 0
0 = 1.82 - (- 0.82) +
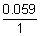
log
10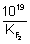
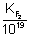
= 8.23 x 10
44 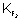
= 8.23 x 10
63Q.3. Show that potential areadditive for process in which half reaction are added to yeild on overall rxn. but they arenot additive when added to yeild a third half rxn.
Ans:
Case - I: When two half rxnx. are added to give an over all rxn., no. of moles of electrons involved in each half rxn. & over all rxn. are necessarily same.
M
1 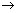
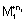
+ n
1e -

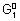
= n
1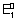
F
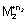
+ n
2e
- 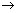
M
2 -

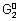
= n
2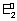
F

M
1 +
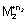
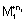
+ M
2 -

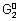
= n
3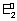
F


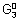
=

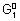
+

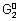
n
3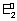
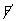
= n
1
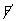
+ n
2E
0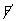
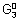
=
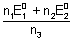
Since n
1 = n
2 = n
3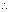
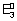
=
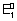
+
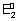 Case - II
Case - II: When n
1 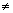
n
2 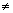
n
3 M
1 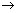
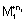
+ n
1e
- -

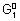
= n
1
F
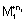
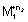
+ (n
2 - h
1)e
- -

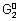
= (n
2 - n
1)
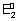
F

M
1 
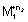
+ n
2e
- -

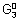
= n
2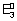
F

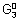
=

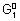
+

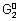
n
2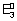
F = n
1 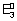
F + (n
2 - n
1)
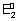
F
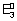
=
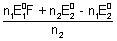 Key Words
Key Words
Electrolysis.
Faraday's law of electrolysis.
Transport No.
Conductance.
Specific Conductance.
Equivalent Conductance.
Molar Conductance.
Kohirausch Law.
EMF.
NErst Eq.
Cellpotential.