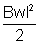Electromagnetic Induction - 2
LENZ’S LAW:
"The direction of any magnetic induction effect is such as to oppose the cause of the effort".
It states that the polarity of the induced e.m.f. and the direction of induced current is such that it opposes the very cause which produces it.
Dumb Question: Is Lenz’s Law an independent law ?
Ans: Lenz’s law is not an independent principle. It gives the same result as the sign rules we interduced in connection with Faraday’s Laws, but is often easier to use. It is directly related to Conservation of Energy.
Illustration: A bar magnet is freely pulling along the axis of a circular loop as show in the figure. State whether its acceleration a is equal to greater than or less than the acceleration due to gravity g ?
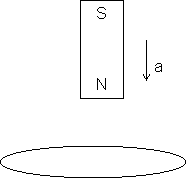
Ans: a < g. Because according to Lenz's law, whatever may be the direction of induced current, it will oppose the cause. There the cause is, the free fall of magnet and so the induced current will oppose it and the acceleration of the will be less than the acceleration due to gravity g.
MOTIONAL E.M.F.:
If the straight conductor is moving in a magnetic field electrons inside it experience a force
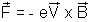
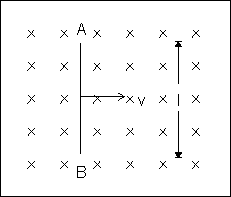
and accumulate at the end of the conductor. Thus, an elecric field(
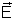 ) is established across its ends. then
) is established across its ends. then 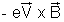 is balanced by - e
is balanced by - e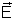 in the opposite direction, at equillibrium.
in the opposite direction, at equillibrium.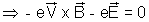
Now E = Induced e.m.f.
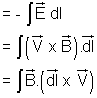
As
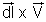 is the swept per unit time by length dl and hence
is the swept per unit time by length dl and hence 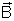 .(
.(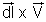 ) is the flux of induction through this area. Therefore the motional e.m.f. is equal to the flux of induction wt by the conductor per unit time. If l, B and V are mutually perpendicular to each other then
) is the flux of induction through this area. Therefore the motional e.m.f. is equal to the flux of induction wt by the conductor per unit time. If l, B and V are mutually perpendicular to each other then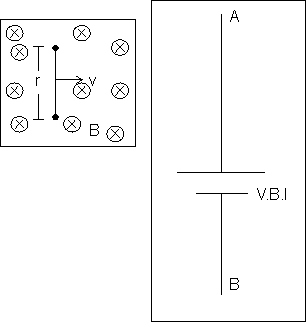
EMF induced = E = BlV
So we can replace the moving rod by a battery of e.m.f. VBl with positive terminal at A and negative terminal at B.
Dumb Question: Suppose if the conductor is not straight then how to find reduced e.m.f. ?
Ans: Suppose the case is as shown
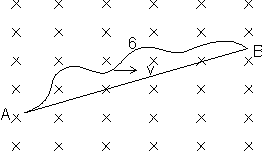
In general we can say that, motional e.m.f. in wire ACB in a uniform magnetic field is the motional e.m.f. in an imaginary wire AB.
Thus EACB = EAB = (length of AB)(V1)B
Here V1 is the component of velocity to both
 and AB>
and AB>Illustration: Find the motional e.m.f. induced in a rod rotating with a uniform angular velocity with uniform magnetic field
 as shown.
as shown.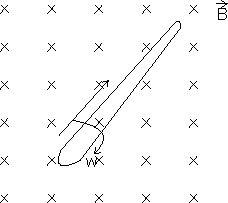
Ans: Consider a small element dr at a distance r a shown.
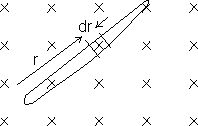
The velocity of this regment = V = rw is
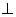 to dr and B.
to dr and B.The induced e.m.f. in this regment = dE = BVdr
 dE= Brw dr
dE= Brw drFor complete rod's induced e.m.f. integrating:
E =
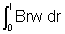
 E =
E = 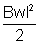
Thus the induced e.m.f. is