Electromagnetic Induction - 7
M5. A coil of L = 50 x 106 H and 5 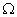 is connected to a t = 5 V. A resistanc of 10
is connected to a t = 5 V. A resistanc of 10 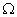 is connected parallel to the coil. Now at some instant the connection of the battery is switched off. Find the amount of heat generated in the coil after switching off the battery ?
is connected parallel to the coil. Now at some instant the connection of the battery is switched off. Find the amount of heat generated in the coil after switching off the battery ?
Ans: Total energy stored in the inductor = 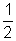 LI02
LI02
EL = 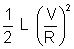
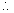 Fraction of energy lost across inductor.
Fraction of energy lost across inductor.
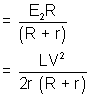
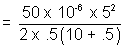
= 1.14 x 10-4 J
H1. Two parrallel rails with negligable resistence 10 cm apart. They are connected by a 5  resistor. The circuit also contains two metal rods having resistances of 10
resistor. The circuit also contains two metal rods having resistances of 10  and 15
and 15  along the rails. The rods are pulled away from the resistor at constant speeds4 m/s and 2 m/s respectively.
along the rails. The rods are pulled away from the resistor at constant speeds4 m/s and 2 m/s respectively.
A uniform magnetic field of magnitude .01 T is applied perpendicular to the plane of the rails. Determine the current in 5
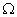 resistor ?
resistor ?Ans: In figure R = 5
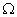 , r1 = 10
, r1 = 10 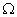 , r = 15
, r = 15 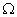 , e1 = 4 x 10-3 V, e2 = 2 x 10-3 V
, e1 = 4 x 10-3 V, e2 = 2 x 10-3 VThe rod ab will act as a source of e.m.f. e1 = BV1l1 = .01 x 4 x .1
= 4 x 10-3
and r1 = 10
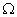
Similarly, ef: e2 = BV2l2
= .01 x 2 x .1
= 2 x 10-3 V
r2 = 15
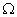
Refer figure (b)
Net resistance of the circuit = r2 +
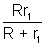
= 15 +
=
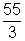 A
A Current I =
Current I = 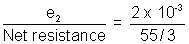
=
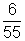 x 10-3 A
x 10-3 A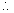 Current through R,
Current through R,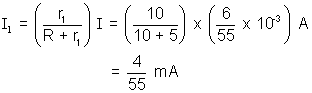
Refer figure (c):
Net resistance = r1 +
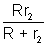
=
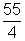
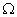
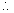 Current I' =
Current I' = 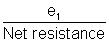
=
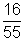 x 10-3 A
x 10-3 A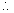 Current through R =
Current through R = 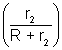 I'
I'=
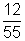 mA
mAFrom superposition principal net current through 5
 resistor is: I' - I =
resistor is: I' - I = 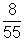 mA from d to c.
mA from d to c.H2. A solenoid has an induction of 10 H and a resistance of 2
 . It is connected to a 10 V battery. How long will ittake for the magnetic energy to reach 1/4 th of itsmaximum value.
. It is connected to a 10 V battery. How long will ittake for the magnetic energy to reach 1/4 th of itsmaximum value.Ans: Let the current through the circuit be I after a time t.
Then
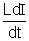 + RI = V
+ RI = Vor,
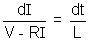
integrating this expression keeping I = 0 at t = 0.
We get: I =
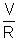 [1 -
[1 - 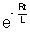 ]
] I = I0(1 -
I = I0(1 - 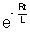 ) ................................................. (1)
) ................................................. (1)where I0 =
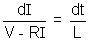 = Maximum Current.
= Maximum Current.Magnetic Enegy Stored =
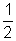 LI2
LI2Here
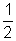 LI2 =
LI2 = 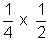 (LI02)
(LI02)or, I =
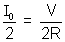
Substituting the values in equation (1) we get:
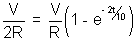
or, .5 = 1 -
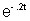
or,
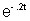 = .5
= .5Which gives t = 3.478 seconds.
Key Words:
1. Magnetic Flux.
2. Faraday's Law.
3. Lenz's Law.
4. Motional E.M.F.
5. Self Induction.
6. Mutual Induction.
7. R - L Circuit.
8. L - C Oscillations.