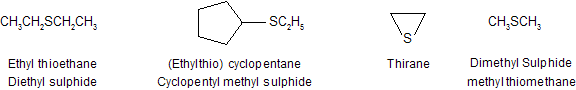Ethers-Epoxides-1
Ether and epoxides
We know alcohols family with their rich chemical reactivity but ethers - compounds containing a R-O- R unit are less reactive and gives relatively few chemical reactions. This lack of reactivity of ether makes them valuable as inert solvents in a number of chemical reactions.
Unlike most ethers, epoxides – compounds in which the C – O – C unit forms a three-membered ring - are very reactive substances due to molecular strain.
Ethers are defined as symmetrical or unsymmetrical depending on whether the two groups bonded to oxygen are the same or different. Unsymmetrical ethers are also called mixed ethers. Dimethyl ether is a symmetrical while ethyl methyl ether is an unsymmetrical ether.
Cyclic ethers have their oxygen as part of a ring. They are heterocyclic compounds. Oxygen heterocycles of commonly encountered ring sizes have specific IUPAC nomenclature.
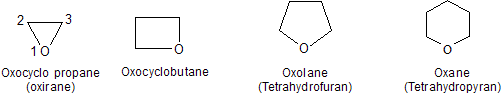
In each case the ring is numbered starting at the oxygen. The IUPAC rules also permit oxirane (without substituents) to be called ethylene oxide. Tetrahydrofuran and tetrahydropyran are acceptable synonyms for oxolane and oxane, respectively.
There are many compounds, often used as reaction solvents, are the diethers 1,2,-dimethoxy ethane and 1,4-dioxane. Diglyme, also a commonly used solvent, is a tri ether.

The sulfur analogs (RS –) of alkoxy groups are called alkyl thio groups while RSH are known as alkane thiol. Sulfur hetero cycles have names analogous to their oxygen relatives, except that ox - is replaced by thi-. Thus the sulfur heterocycles containing three-, four-, five-, and six- membered rings are named thiirane, thietane, thiolane, and thiane, respectively.