Ethers-Epoxides-5
Overall Reaction :
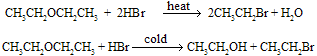
Mechanism of reaction
Step A : Ether reacts with proton to give a dialkyloxonium ion (oxonium salt)
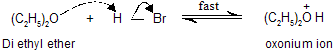
Step B : Halide attack on carbon of the dialkyloxonium ion. This step gives each molecule of an alkyl halide and an alcohol.
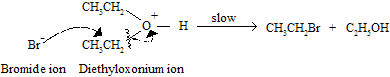
Step C : In last step where an alcohol is converted to an alkyl halide.
(iii) Reaction with HI (fission reaction)
Reaction with HI is an example of fission reaction where cleavage is decided by structure of ether. If there is smaller alkyl group up to secondary than fission is SN2 so back attack of nucleophile occurs while for large alkyl group always fission by SN1 mechanism because they prefer carbocation mechanism.
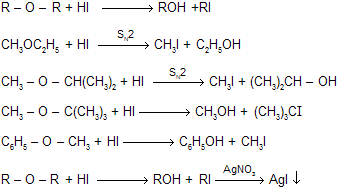 |
When ethers reacts with cold HI to form one mole of alkyl iodide. This when reacts with silver nitrate to form yellow precipitate of AgI.
By finding out the weight of AgI we can find out the structure of ether. This method is known as of zeisal’s method for estimation of alkoxy group in the molecule for example.
Problem 0.74 gm of methyl ether forms 2.35 gm of AgI at NTP find out sturcture of methyl ether ?

(iv) Reaction with dil H2SO4
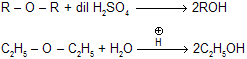 |
(v) Reaction with CO
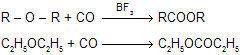 |