Ethers-Epoxides-6
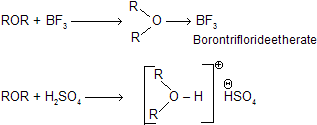
(vi) Reaction with Lewis Acids when reacts with Lewis acid to form acid base complex (oxonium salt.)
 |
(vii) Oxidation with acidic K2Cr2O7
Epoxides (cyclic ether)
Preparation
There are two main laboratory methods for the preparation of epoxides :
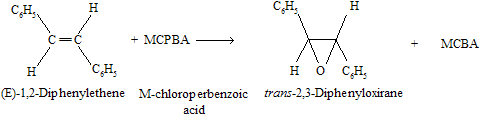
(1) Epoxidation of alkenes by reaction with peroxy acids
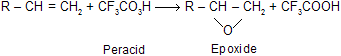
The reaction is easy to carry out, and yields are usually high. Epoxidation is a stereospecific syn addition.
(2) Conversion of vicinal halohydrins to epoxides
The formation of vicinal halohydrins from alkenes was already described in hydrocarbon. Halohydrins are readily converted to epoxides on treatment with base.
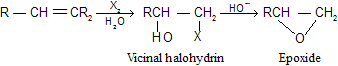
Properties
The chemical property that differ epoxide from normal inert ether is their far greater reactivity toward nucleophilic reagents compared to simple ethers. This high reactivity results from the ring strain of epoxides.
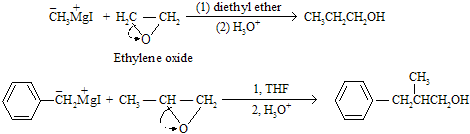
An example of nucleophilic ring opening of epoxides in Grignard reagent, where Grignard reagents with ethylene oxide is used to steeping up in alcohol series.
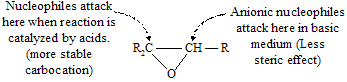
Nucleophiles other than Grignard reagents also responsible for ring opening of epoxides. There are two medium in which these reactions are carried out. The first involves anionic nucleophiles in neutral or basic solution.
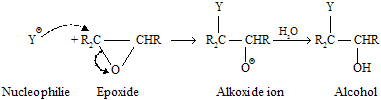
These reactions are carried out in water or alcohols as solvents, and the alkoxide ion intermediate is rapidly changes in to an alcohol by proton transfer.
Nucleophilic ring-opening reactions of epoxides may also be catalysed by acidic medium where the nucleophile is not an anion but rather a solvent molecule.
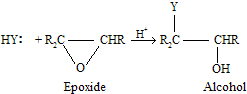
There is very important difference in the ring-opening chemistry of epoxides depending on the reaction medium. Unsymmetrically substituted epoxides tend to react with anionic nucleophiles in basic medium at the less hindered carbon of the cycle. While under conditions of acid catalysis, the more highly substituted carbon is attacked because partial carbocation character comes in this condition so molecule tends to prefer more stable intermediate.