Absolute Value of Modulus Function:
y = |x| = 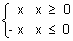
Domain 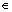 R Range R Range 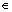 (0, (0, 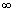 ) )
Properties of modulus function:
(i) |x| 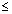 a a 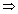 - a - a 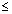 x x 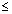 a (a a (a 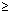 0) 0)
(ii) |x| 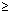 a a 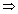 x x 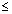 - a or x - a or x 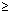 a (a a (a 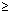 ) )
(iii) |x + y| 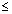 |x| + |y| |x| + |y|
(iv) |x + y| 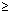 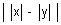
Illustration: Find domain of y = 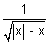
Ans: y is defind if (|x| - x) > 0
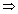 |x| > x which hold for -ve x only |x| > x which hold for -ve x only
Hence domain (- 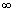 , 0) , 0)
(7) Signum Function:
y = Sgn(x) = 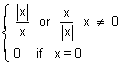
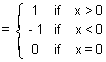
Domain x  R R
Range  {- 1, 0, 1} {- 1, 0, 1}
(8) Greatest integer function:
[x] indicates integral part of x which is nearest & smaller integer to x. It is also c/d floor of x or stepwise function.
[2.3] = 2 [5] = 5, [- 0.6] = - 1
In general
n 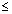 n < n + 1 (n n < n + 1 (n 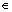 Integer) Integer)
[n] = n
| x | [x] | 0 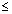 x < 1 x < 1
1 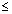 x < 2 x < 2
2 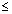 x < 3 x < 3
- 1 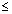 x < 0 x < 0
- 2 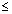 x < - 1 x < - 1 | 0
1
2
- 1
- 2 |
Properties of greatest integer function:
(i) [x] = x holds if x 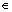 I I I I 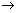 Integer. Integer.
(ii) [x + I] = [x] + I if I is integer.
(iii) [x + y] 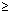 [x] + [y] [x] + [y]
(iv) If [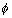 (x)] (x)] 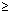 I, then I, then 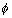 (x) (x) 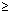 I. I.
(v) If [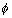 (x)] (x)] 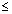 I, then I, then 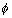 (x) < I + 1 (x) < I + 1
(vi) If [x] > n 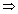 x x 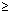 n + 1, n n + 1, n 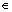 I. I.
(vii) [- x] = - [x] if x 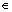 I I
& [- x] = - [x] - 1 if x 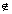 I. I.
(viii) [x + y] = [x] + [x + y - [x]] for all x, y 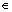 R. R.
(ix) [x] + 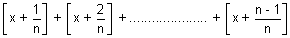
= [n x], n 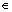 N N N N 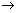 natural no. natural no.
Illustration: y = 2[x] + 3 & y = 3[x - 2] + 5 then find value of [x + y].
Ans: 2[x] + 3 = 3[x - 2] + 5
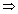 2[x] + 3 = 3[x] - 6 + 5 2[x] + 3 = 3[x] - 6 + 5 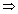 [x] = 4 [x] = 4
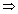 4 4 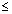 < 5 < 5
x = 4 + f (f 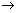 fraction) fraction)
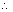 y = 2[x] + 3 = 11 y = 2[x] + 3 = 11
 [x + y] = [4 + f + 11] = [15 + f] = 15 [x + y] = [4 + f + 11] = [15 + f] = 15
(9) Fractional part function:
y = {x}
Let x = I + f, I = [x] & f = {x}
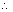 y = {x} = x - [x] y = {x} = x - [x]
| x | {x} | 0  x < 1 x < 1
1  x < 2 x < 2
2 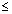 x < 3 x < 3
- 1 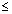 x < 0 x < 0
- 2 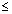 x < - 1 x < - 1 | x
x - 1
x - 2
x + 1
x + 2 |
Domain x 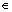 R R
Range (0, 1)
Properties of fraction part of x
(i) {x} = x if 0 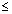 < 1 < 1
(ii) {x} = 0 if x 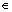 I I
(iii) {- x} = 1 - {x} if x 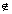 I I
Illustration: Prove that [x] + [y] 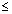 [x + y] where x = [x] + {x} [x + y] where x = [x] + {x}
Ans: x + y = [x] + {x} + [y] + {y}
[x + y] = [[x] + [y] + {x} + {y}]
= [x] + [y] + [{x} + {y}] [By [x + I] = [x] + I]
[x + y] 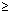 [x] + [y] [x] + [y]
(10) Exponential Function:
f(x) = ax, a > 0, a 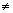 1 1
Domain 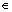 R R
Range 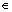 (0, (0, 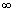 ) )
Case I: a > 1
f(x) = ax increase with increase in x.
i.e. f(x) is increasing function ob R
Case II: 0 < a < 1
f(x) = ax decrease with increase in x
Dumb Question: How range comes out (0, 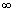 ) ? ) ?
Ans: y = ax
Let a > 1
As x  
Since a > 1
So, ax  
and when x  - - 
ax  0 0
 range (0, range (0, 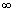 ) )
Logorithmic function:
f(x) = logax (x, a > 0) & a 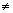 1 1
Domain 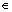 (0, (0, 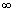 ) )
Range 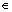 R R
Properties:
(i) Logaa = 1 (ii) logbm a = 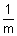 logba {a, b > 0, b logba {a, b > 0, b 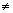 1 m 1 m 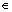 R} R}
(iii) logab = 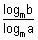 {a, b > 0, a, b {a, b > 0, a, b 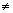 1 & m > 1} 1 & m > 1}
(iv) 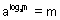 {a, m > 0 & a {a, m > 0 & a 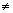 1} 1}
(v) 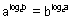 {a, b, c > 0 & c {a, b, c > 0 & c 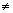 1} 1}
(vi) logma < b 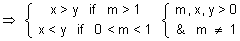
(vii) logma < b 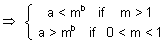
Dumb Question: Why b 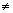 1 in logba ? 1 in logba ?
Ans: logba = c 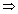 bc = a bc = a
if b = 1
1c 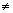 a a
Now whatever value of c, 1c 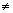 a, so, b a, so, b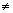 1 1
Illustration: Find domain of f(x) = log10(1 + x3)
Ans: f(x) = log10(1 + x3) exists if
1 + x3 > 0
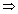 (1 + x)(1 - x + x2) > 0 (1 + x)(1 - x + x2) > 0
But 1 - x2 + x2 > 0 as D < 0 & a > 0
So, 1 + x > 0
x > - 1
x 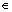 (- 1, (- 1, 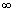 ) )
Trignometric Function:
(1) Sine Function:
f(x) = sinx
Domain 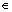 R R
Range [-1, 1]
(2) Cosione Function:
f(x) = cos x
Domain 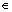 R R
Range [-1, 1]
|
|
| |
|
|