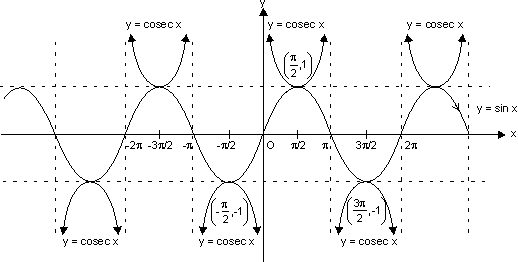
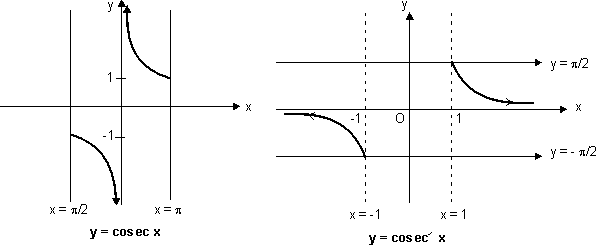
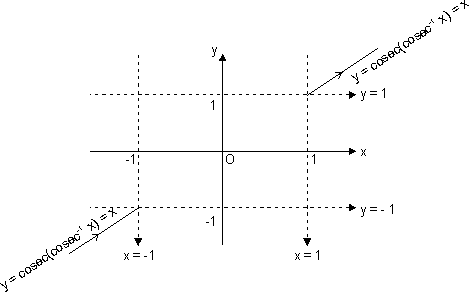Functions an Graphs 3: cosec x graph
(3) Tangent Function:
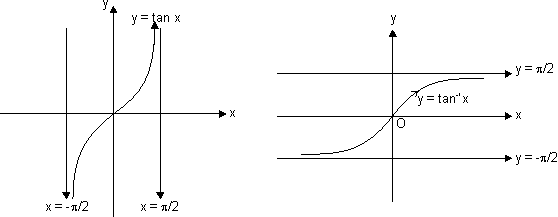
f(x) = tan x
Domain R - {(2n + 1)
R - {(2n + 1) 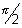 }
}
Range R
R
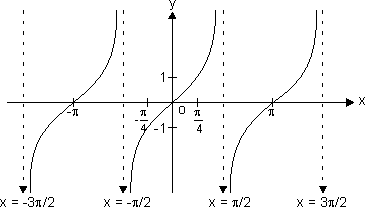
y = tan x increases strictly from - to
to 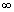 as x increases from -
as x increases from - 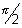 to
to 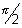 ,
, 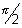 to
to 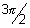
x = ±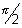 , ±
, ± 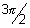 , .......... are asymptotes to y = tan x.
, .......... are asymptotes to y = tan x.
Dumb Question: What is asymptotes ?
Ans: A curve which is tangent to given curve at infinity.
(d) Coecant function:
f(x) = cosec x
Domain R - {n
R - {n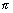 | n
| n  I}
I}
Range R - (- 1, 1)
R - (- 1, 1)
n = n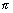 n
n  I is asymptote to y = cosec x
I is asymptote to y = cosec x
(e) Secant Function:
f(x) = sec x
Domain R - {(2n + 1)
R - {(2n + 1) 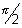 | n
| n  I}
I}
Range R - (- 1, 1)
R - (- 1, 1)
x = (2n + 1)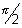 , n
, n  I are asymptote to y = sec x.
I are asymptote to y = sec x.
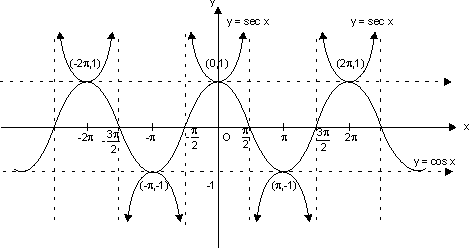
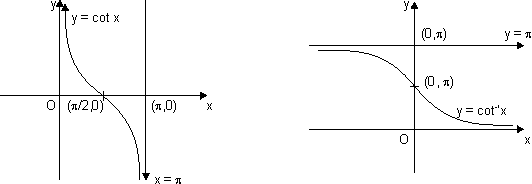
(f) Cotangent Function:
f(x) = cot x
Domain R - {n
R - {n | n
| n  I}
I}
Range R
R
It has x = n n
n  I as asymptotes.
I as asymptotes.
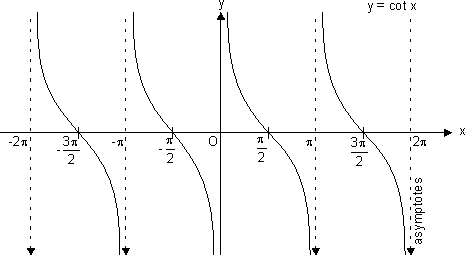
Inverse Function:
(i) Graph of y = sin-1 x;
where
x [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]
and y
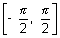
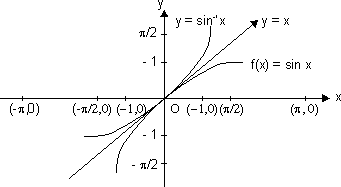
As the graph of f-1 is mirror image of f(x) about y = x.
(ii) Graph of y = tan-1x;
Here,
Domain [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]
Range [0,
[0,  ]
]
(iii) Graph of y = tan-1x;
Here ,
Domain R
R
Range
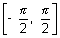 .
.
(iv) Graph of y = cot-1x;
We know that the function f:(0,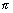 )
)  R, given by f(
R, given by f(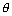 ) = cot
) = cot 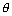 is invertible.
is invertible.
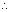 Thus, domain of cot-1x
Thus, domain of cot-1x  R and Range
R and Range  (0,
(0, 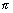 ).
).
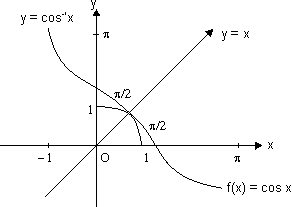
(v) Graph for y = sec-1x;
The function f : [0, ] -
] - 
 (-
(- 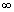 , - 1)
, - 1) 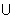 [1,
[1, 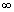 ] given by f(
] given by f(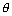 ) = sec
) = sec 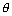 is invertible.
is invertible.
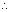 y = sec-1x, has domain
y = sec-1x, has domain  R - (- 1, 1) and range
R - (- 1, 1) and range  [0,
[0, 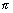 ] -
] - 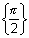 : shown as
: shown as
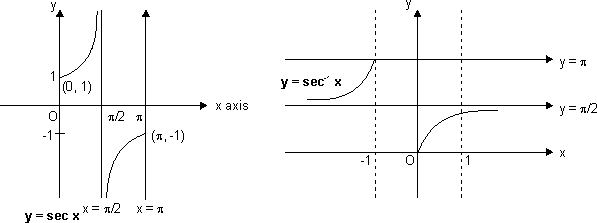
(vi) Graph for y = cosec-1x;
As we know, f: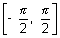 - {0}
- {0}  (- 1, 1) is invertible given by f(
(- 1, 1) is invertible given by f( ) = cos
) = cos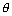 .
.
y = cosec-1x; domain R - (- 1, 1)
R - (- 1, 1)
Range
 - {0}>
- {0}>
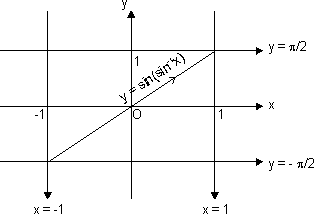
Sketch of y = sin(sin-1x):
Domain x [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]
and range y = x y
y  [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]
Sketch y = sin(sin-1x) only
when x [-1, 1] & y = x
[-1, 1] & y = x
Sketch of curve y = cos(cos-1x):
Domain x [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]
and range y = x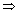 y
y  [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]
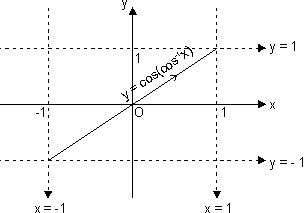
Sketch of curve y = tan(tan-1x):
Domain, x R
R
Range y = x y r
r
We should sketch
y = tan(tan-1x) = xv x  R
R
Sketch of curve y = cosec(cosec-1x):
Domain x R - (-1, 1)
Range y = x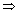 y
y  R - (-1, 1)
R - (-1, 1)
y = cosec(cosec-1x) = x only
when x (-
(-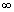 , -1)
, -1) 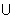 (1,
(1, 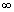 )
)
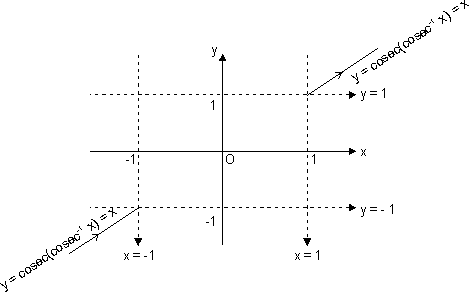
f(x) = tan x
Domain
 R - {(2n + 1)
R - {(2n + 1) 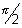 }
}Range
 R
R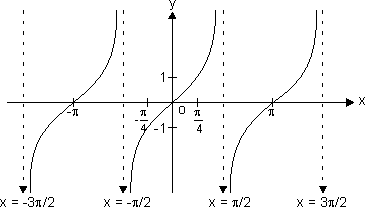
y = tan x increases strictly from -
 to
to 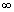 as x increases from -
as x increases from - 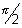 to
to 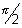 ,
, 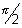 to
to 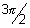
x = ±
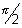 , ±
, ± 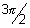 , .......... are asymptotes to y = tan x.
, .......... are asymptotes to y = tan x.Dumb Question: What is asymptotes ?
Ans: A curve which is tangent to given curve at infinity.
(d) Coecant function:
f(x) = cosec x
Domain
 R - {n
R - {n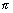 | n
| n  I}
I}Range
 R - (- 1, 1)
R - (- 1, 1)n = n
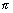 n
n  I is asymptote to y = cosec x
I is asymptote to y = cosec x
(e) Secant Function:
f(x) = sec x
Domain
 R - {(2n + 1)
R - {(2n + 1) 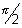 | n
| n  I}
I}Range
 R - (- 1, 1)
R - (- 1, 1)x = (2n + 1)
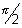 , n
, n  I are asymptote to y = sec x.
I are asymptote to y = sec x.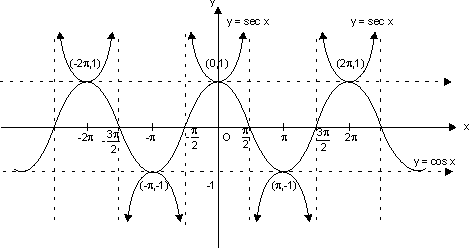
(f) Cotangent Function:
f(x) = cot x
Domain
 R - {n
R - {n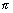 | n
| n  I}
I}Range
 R
RIt has x = n
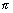 n
n  I as asymptotes.
I as asymptotes.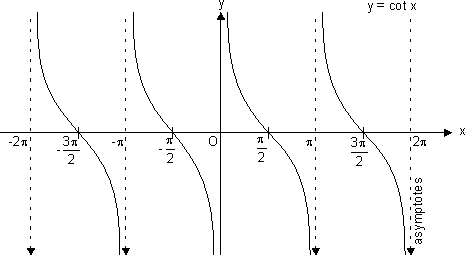
Inverse Function:
(i) Graph of y = sin-1 x;
where
x
 [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]and y

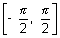
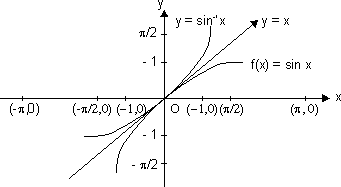
As the graph of f-1 is mirror image of f(x) about y = x.
(ii) Graph of y = tan-1x;
Here,
Domain
 [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]Range
 [0,
[0, 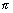 ]
]
(iii) Graph of y = tan-1x;
Here ,
Domain
 R
RRange

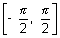 .
.
(iv) Graph of y = cot-1x;
We know that the function f:(0,
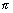 )
)  R, given by f(
R, given by f(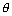 ) = cot
) = cot 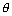 is invertible.
is invertible. Thus, domain of cot-1x
Thus, domain of cot-1x  R and Range
R and Range  (0,
(0, 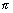 ).
).
(v) Graph for y = sec-1x;
The function f : [0,
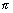 ] -
] - 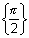
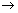 (-
(- 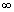 , - 1)
, - 1) 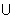 [1,
[1, 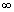 ] given by f(
] given by f(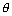 ) = sec
) = sec 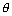 is invertible.
is invertible.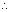 y = sec-1x, has domain
y = sec-1x, has domain  R - (- 1, 1) and range
R - (- 1, 1) and range  [0,
[0, 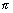 ] -
] - 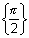 : shown as
: shown as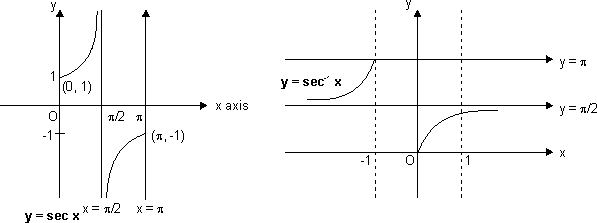
(vi) Graph for y = cosec-1x;
As we know, f:
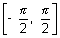 - {0}
- {0}  (- 1, 1) is invertible given by f(
(- 1, 1) is invertible given by f( ) = cos
) = cos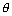 .
.y = cosec-1x; domain
 R - (- 1, 1)
R - (- 1, 1)Range

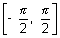 - {0}>
- {0}>
Sketch of y = sin(sin-1x):
Domain x
 [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]and range y = x
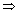 y
y  [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]Sketch y = sin(sin-1x) only
when x
 [-1, 1] & y = x
[-1, 1] & y = x
Sketch of curve y = cos(cos-1x):
Domain x
 [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]and range y = x
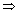 y
y  [-1, 1]
[-1, 1]
Sketch of curve y = tan(tan-1x):
Domain, x
 R
RRange y = x y
 r
rWe should sketch
y = tan(tan-1x) = x
 R
R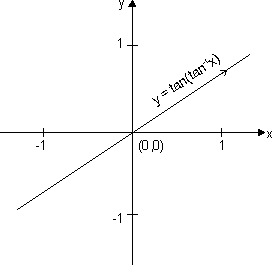
Sketch of curve y = cosec(cosec-1x):
Domain x R - (-1, 1)
Range y = x
 y
y  R - (-1, 1)
R - (-1, 1)y = cosec(cosec-1x) = x only
when x
 (-
(- , -1)
, -1)  (1,
(1,  )
)