Functions:
Illustration: Find no. of surjection from A
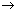
B
A = {1, 2, 3, 4} & B = {a, b}
Ans:
1

2 images
2

2 images
3

2 images
4

2 images
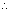
Total no. of function = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2
4But there are two function f(x) = a for all x

A & g(x) = b for all x

A are not surjective.
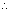
Total no. of surjection from A to B = 2
4 - 2 = 14
Inverse function: Let f : A
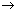
B be one-one & onto function then there exists a unique function.
g : B
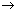
A such that f(x) = y
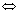
g(y) = x,
v x

A & y

B
Then g is c/d inverse of F.
So, g = f
-1 : B
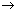
A = {(f(x), x) | (x, f(x)

f}
Domain of f = {1, 2, 3, 4} = range of f
-1Range of f = {2, 4, 6, 8} = domain of f
-1.
Illustration: If f(x) = 3x - 5, then find f
-1(x).
Ans: f(x) = 3x - 5 which linear function so bijective.
Let f(x) = y

Y = 3x - 5

x =
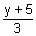

f
-1(y) =
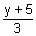

f
-1(x) =
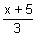 Note
Note: (1) Graph of y = f(x) and y = f
-1(x) are mirror images to each other.
(2) If f : A
B & g : B
C are two bijections, then gof : A
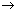
C is bijection & (gof)
-1 = (f
-1og
-1).
(3) If fog = gof then either f
-1 = g or g
-1 = f and (fog)(x) = (gof)(x) = (x)
Easy Type
Q.1. Find domain of f(x) = log
10log
10(1 + x
3)
Ans: Let log
10(1 + x
3) = y
f(x) = log
10y

y > 0

log
10(1 + x
3) > 0

(1 + x
3) > 10
0
x
3 > 0

x

(0,
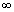
)
Q.2. Find domain of y =
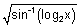
Ans: Let log
2x = z
z is defined if x > 0 .......................................... (i)
and - 1

z

1 or - 1

log
2x

1

1/2

x

2 ................................................. (ii)
But y is defined if
sin
-1z
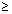
0 or sin
-1log
2(x)
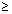
0 ..................... (iii)


log
2x
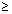
0

x
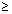
2
0 
x
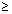
1 .................. (iv)
From (i), (ii) & (iv)
1

x

2
domain x

[1, 2]
Q.3. Find values of 'a' for which f(x) = tan
-1(x
2 - 18x + 9) > 0 for x

R.
Ans: f(x) > 0
v x

R

x
2 - 18x + a > 0
v x

R
ax
2 + bx + c > 0 if D < 0 & a > 0
D = (18)
2 - 49 < 0

a > 81

a

(81,
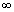
)
Q.4. f(x) =
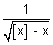
find domain of f9x).
Ans: f(x) =
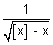
exists if
[x] - x > 0

[x] > x
But by definition of greatest integer function
[x]

x as x = [x] + {x}
So, it is not possible that [x] > x
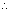
domain f(x) =
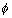
Q.5. Solve 4{x} = x + [x]
Ans: x = [x] + {x}
4{x} = [x] + {x} + [x]

{x} =
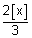
But 0

{x} < 1
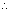
0

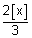
< 1

0

[x] < 3/2
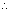
[x] = 0 or 1
If [x] = 1, then {x} = 2/3
Thus, x = [x] + {x} = 1 + 2/3 = 5/3
If [x] = 0, {x} = 0
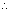
x = 0
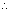
Solutions x

{0, 5/3}
Q.6. Find range for y =
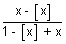
.
Ans: y =
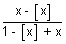
=
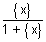
Domain

R
y =
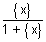

{x} =
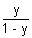
Since 0

{x} < 1

0

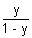
< 1

0

y < 1/2
range = (0, 1/2)
Q.7. Let f(x) be periodic & k bca +ve real no. such that f(x + k) + f(x) = 0
v x

R. Prove that f(x) f(x) is periodic with period 2k.
Ans: f(x + k) + f(x) = 0
v x

R
f(x + k) = - f(x)
v x

R ................................................... (i)
put x = x + k

f(x + 2k) = -f(x + k)
v x

R
from (i)
f(x + 2k) = f(x),
v x

R
f(x) is peruiodic with period 2k.
Q.8. Find period of f(x) = tan3x + sin
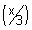
Ans: Period for tan 3x is
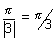
Period for sin
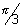
is |2
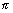
x
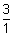
= 6
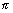
LCM of
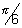

sin
-1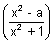
<
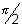

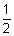

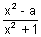
< 1

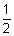

1 -
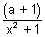
< 1,
v x

R

-
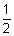

-
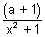
< 0

a + 1 > 0

a

(-1,
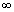
)
Q.10. If f : R
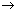
R f(x) = x
2 + 1, then find value of f
-1(17).
Ans: f(x) = x
2 + 1
f
-1(17)

f(x) = 17

x
2 + 1 = 17

x = ±4
x = {4, -4}
Medium Type
Q.1. Find domain of function. f(x) =
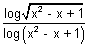
Ans: log(x
2 - x + 1) is defined when
x
2 - x + 1 > 0 & x
2 - x + 1
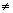
1

x

R and x
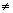
0, 1

x

R - {0, 1} ..................................... (i)
[
Dumb Question: How x
2 - x + 1 > 0
v x

R & why x
2 - x + 1
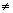
1 ?
Ans: ax
2 + bx + c > 0
v x

R if a > 0 & D < 0
For x
2 - x + 1, a = 1 > 0 & D = 1 - 4 = - 3 < 0
So, x
2 - x + 1 > 0 for all x

R
& If x
2 - x + 1 = 1 then logx
2 - x + 1 = 0
&
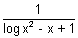
=
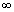
which is not desired.]
Again log(sin
-1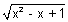 )
) exists when x
2 + x + 1 > 0 & x
2 + x + 1

1
i.e. 0 < x
2 + x + 1

1

x
2 + x

0

x

[-1, 0] .............................. (ii)
From (i) & (ii)
x

[-1, 0)
Q.2. Find domain of f(x) =
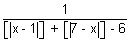
where {} is greatest integer function.
Ans: f(x) is defined when
[|x - 1|] + [|7 - x|] - 6
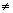
0
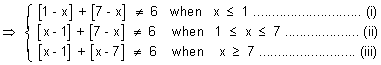
Taking (i)
[1 - x] + [7 - x]
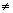
6

1 + [-x] + 7 + [-x]
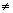
6

2[-x]
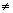
- 2 [-x]
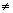
- 1

x
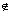
(0, 1] ................................... (1)
From (ii)
[x - 1] + [7 - x]
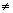
6

[x] - 1 + 7 + [-x]
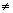
6

[x] + [-x]
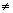
0 x
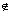
Integer

x
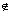
{1, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} ................. (2)
From (iii)
x

[7, 8) ..................................... (3)
From (1), (2) & (3)
Domain f(x)

R - {(0, 1]
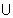
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
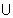
[7, 8)}
Q.3. f(x, y) is periodic function satisfying condition f(x, y) = f((2x + 2y),(2y - 2x))
v x,y

R. Now g(x) = f(2
x, 0) then prove that g(x) is periodic function, find its period.
Ans: f(x, y) = f(2x + 2y, 2y - 2x) ....................................... (i)
Put x = 2x + 2y & y = 2y - 2x

f(2x + 2y, 2y - 2x) = f(2(2x + 2y) + 2(2y - 2x), 2(2y - 2x) - 2(2x + 2y)) [By (i)]

f(x, y) = f(2x + 2y, 2y - 2x) = f(8y, - 8x)

f(x, y) = f(8y, - 8x) ..................................................... (ii)

f(8y, - 8x) = f{8(- 8x), - 8(8y)} [By (ii)]

f(x, y) = f(2x + 2y, 2y - 2x) = f(8y, - 8x) = f(- 64x, - 64y)

f(x, y) = f(- 64x, - 64y) ............................................... (iii)

f(- 64x, - 64y) = f(64 x 64 x, 64 x 64y) = f(2
12x, 2
12y) [By (iii)]

f(x, y) = f(2
12x, 2
12y)

f(2
x, 0) = f(2
12.2
x, 0) = f(2
12 + x, 0)

g(x, 0) = f(2
x, 0) = f(2
12 + x, 0)

g(x, 0) = g(x + 12, 0)

g(x) is periodic with period
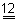
Q.4. Let f(x) =
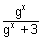
. Show that f(x) + f(1 - x) = 1 & hence, evaluate
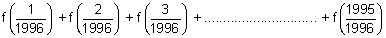
Ans: f(x) =
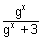
................................................. (i)
and f(1 - x) =
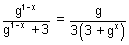
.............................. (ii)
Adding (i) & (ii), we get
f(x) + f(1 - x) =
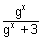
+
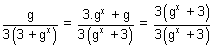
f(x) + f(1 - x) = 1 ............................................. (iii)
Now, putting x =
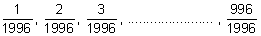
in (iii).
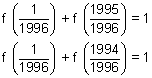
........................
........................
........................
........................
........................
........................
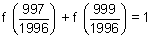
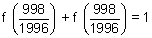
or
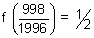
Adding all.
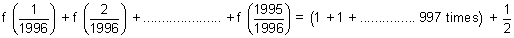
[
Dumb Question: For what
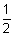
is added ?
Ans: For
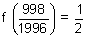
]
= 997 +
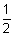
= 997.5
Q.5. Let g(x) be inverse of f(x) and f'(x) =
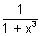
. Then find g'(x) in terms of g(x).
Ans: Since g(x) is inverse of f(x)
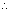
(gof)(x) = x

g{f(x)} = x

g'{f(x)} f'(x) = 1

g'{f(x)} =
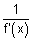
= 1 + x
3
g'{f(g(x))} = 1 + (g(x))
3
g'(x) = 1 + (g(x))
3Dumb Question: How f(g(x)) = x ?
Ans: Since g(x) is inverse of f(x)
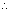
f(x) is also inverse of g(x)
By inverse property
f(g(x)) = x