Hard Type
Q1. Prove that a2 + b2 + c2 + 2abc < 2 where a, b, c, are sides of 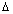 ABC such that a + b + c = 2 ABC such that a + b + c = 2
Ans: a + b + c = 2
 1 - a + 1 - b + 1 - c = 1 1 - a + 1 - b + 1 - c = 1
 x + y + z = 1 where x = 1 - a, y = 1 - b, z = 1 - c x + y + z = 1 where x = 1 - a, y = 1 - b, z = 1 - c
Sine in 
Sum of two sides > third side
a + b > c  0 < c < 1 0 < c < 1
Similarly 0 < a, b < 1
hence 0 < x, y, z < 1
Now,
a2 + b2 + c2 + 2abc = (1 - x)2 + (1 - y)2 + (1 - z)2 + 2(1 - x)(1 - y)(1 - z)
= 3 - 2(x + y + z) + x2 + y2 + z2 + 2{1 - (x + y + z) + (xy + yz + zx) - xyz}
= 1 + x2 + y2 + z2 - 2xyz + 2(xy + yz + zx)
= 1 + (x + y + z)2 - 2xyz
= 2 - 2xyz < 2 as 0 < x, y, z < 1
 a2 + b2 + c2 + 2abc < 2 a2 + b2 + c2 + 2abc < 2
Dumb Question: How 0 < c < 1 ?
Ans: Since gn  , ,
Sum of two sides > third side
a + b > c ............................................. (i)
or a + b + c > 2c
2 > 2c  c < 1 ..................................... (ii) c < 1 ..................................... (ii)
Since c is side of 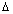
 c > 0 ............................................... (iii) c > 0 ............................................... (iii)
 From (ii) & (iii) From (ii) & (iii)
0 < c < 1
Q.2. A function R 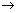 R is f(x) = R is f(x) = 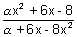 . Find integral value of . Find integral value of  for which f is onto. for which f is onto.
Ans: Since f : R  R is onto mapping R is onto mapping
 Range = codomain = R Range = codomain = R
 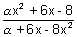 assumes all real values of x assumes all real values of x
Let y = 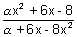
 x2( x2( + 8y) + 6x(1 - y) - (8 - + 8y) + 6x(1 - y) - (8 -  y) = 0 y) = 0 v y 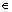 R R
 D D 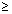 0 0
36(1 - y)2 + 4( + 8y)(8 + + 8y)(8 +  y) y) 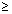 0 0
 [y2(8 [y2(8 + 9) + y( + 9) + y( 2 + 46) + (8 2 + 46) + (8 + 9) + 9) 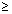 0 0
ax2 + bx + c 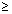 0 0 v x 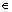 R if a > 0 & D R if a > 0 & D 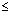 0 0
( 2 + 46)2 - 4(8 2 + 46)2 - 4(8 + 9)(8 + 9)(8 + 9) + 9) 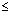 0 & (8 0 & (8 + 9) > 0 + 9) > 0
 ( ( 2 + 46)2) - [2(8 2 + 46)2) - [2(8 + 9)]2 + 9)]2 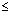 0 & 0 &  > - > - 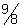
 ( ( 2 + 46 - 16 2 + 46 - 16 - 18)( - 18)( 2 + 46 + 16 2 + 46 + 16 + 18) + 18) 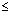 0 & 0 &  > - > - 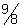
 ( ( - 14)( - 14)( - 2)( - 2)( + 8)2 + 8)2 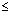 0 and 0 and  > - > - 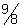
  [2, 14] [2, 14] 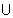 {-8} and {-8} and  > - > - 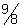
  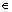 [2, 14] [2, 14]
Q.3. Solve the eq. [x]{x} = x
Ans: x = [x] + {x} .................................. (i)
 [x]{x} = [x] + {x} [x]{x} = [x] + {x}  {x} = {x} = 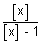 ............................. (ii) ............................. (ii)
[x] 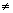 1 in eq. (ii) 1 in eq. (ii)
But if [x] = 1, then
{x} = x which is donje only when,
x 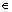 [0, 1) ................................................. (iii) [0, 1) ................................................. (iii)
& [x] = 1  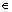 [1, 2) ................................. (iv) [1, 2) ................................. (iv)
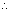 From (iii) & (iv) no value of x, From (iii) & (iv) no value of x,
when [x] = 1
As we know
{x} 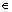 [0, 1) [0, 1)
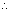 0 0 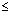 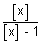 < 1 < 1
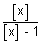 < 1 & < 1 & 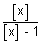  0 0
 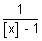 < 0 & {[x] < 0 & {[x] 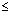 0 or [x] > 1} 0 or [x] > 1}
 [x] < 1 & {[x] [x] < 1 & {[x] 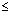 0 or [x] > 1} 0 or [x] > 1}
 [x] [x] 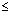 0 0
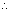 x = [x] + {x} = [x] + x = [x] + {x} = [x] + 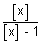
x = 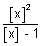 , where x takes values less than 1. , where x takes values less than 1.
 x = x = 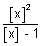 , where x < 1 , where x < 1
x = 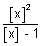 , where [x] is any non positive integer. , where [x] is any non positive integer.
Q4. Sketch y = (x - 1)(x - 2)
Ans: y = (x - 1)(x - 2)
(i) put y = 0  x = 1, 2 x = 1, 2
(ii) y = x2 - 3x + 2
 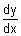 = 2x - 3 & = 2x - 3 & 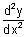
as 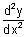 > 0 > 0
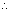 minimaq at x = 3/2. minimaq at x = 3/2.
(iii) Increases when x > 3/2 & decreases when x < 3/2.
y = x2 - 3x + 2
when x = 3/2
y = 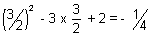
Q5. Sketch curve y = (x - 1)(x - 2)(x - 3)
Ans: y = (x - 1)(x - 2)(x - 3)
(i) Put y = 0  x = 1, 2, 3 x = 1, 2, 3
(ii) y = x3 - 6x2 + 11x - 6
 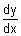 = 3x2 - 12x + 11 & = 3x2 - 12x + 11 & 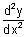 = 6x - 12 = 6x - 12
when 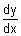 = 0 = 0  x = x = 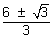
Maxima when x = 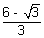 as as 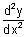 = - 2 = - 2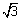
Minima when x = 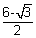 as as 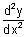 = 2 = 2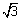
(iii) 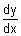 = 3x2 - 12x + 11 = 3x2 - 12x + 11
= 3(x - 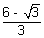 )(x - )(x - 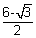 ) )
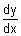 > 0 or Increases when > 0 or Increases when
x < 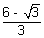 or x > or x > 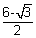
Decreases when 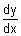 < 0 < 0
or 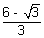 < x < < x < 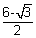
(iv) Concave upwards when x > 2 & concave down when x < 2.
x = 2 is point where concavity of curve changes.
Key Words:
* Function.
* Domain.
* Codomain.
* Range.
* Identity Function.
* Constant Function.
* Logarithmic Function.
* Modulus Function.
* Signum Function.
* Greatest Integer Function.
* Fractional Part Function.
* Odd & Even Function.
* Periodic Function.
* Composite Function.
* Mapping.
* Bijective.
* Surjective.
* Injective.
* Inverse of Function. |
|
| |
|
|