fundamentals-of-organic-chemistry-2
(ii) Nucleophilic addition reaction
These type of reaction are given by carbonyl compounds (aldehydes & ketones) where primary attack of nucleophile takes place due to more stability of intermediate species. >C = O always exist in polar form where carbon with +ve charge while oxygen contains –ve charge.
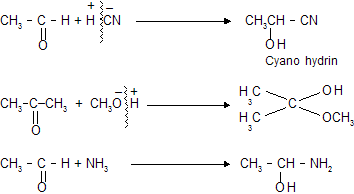
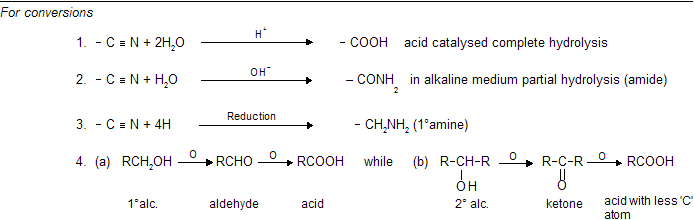
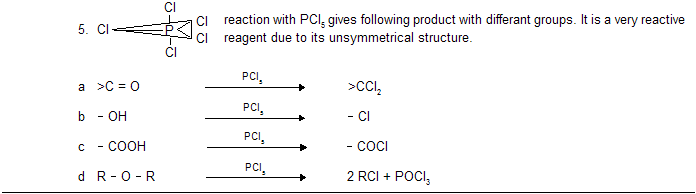
(iii) Nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN type)
These type of reactions occurs in by alkyl halides, aryl halides, acids and their derivatives where attack of nucleophile takes place on
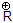 and halogen comes out as leaving group.
and halogen comes out as leaving group.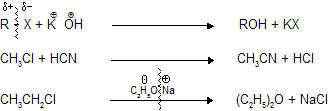
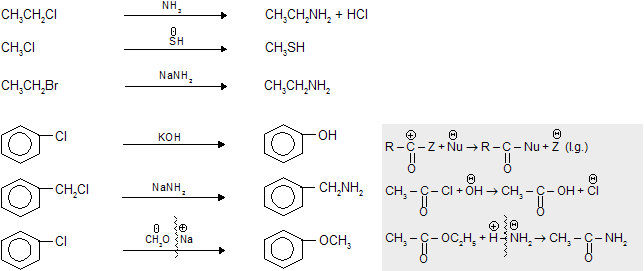
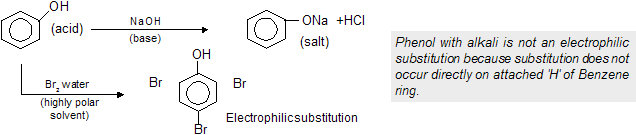
(iv) Electrophilic substitution reaction (SE type)
Given by Aromatic compounds and their derivatives where high
 density is present with delocalisation of electrons so the compound prefers substitution rather than addition.
density is present with delocalisation of electrons so the compound prefers substitution rather than addition.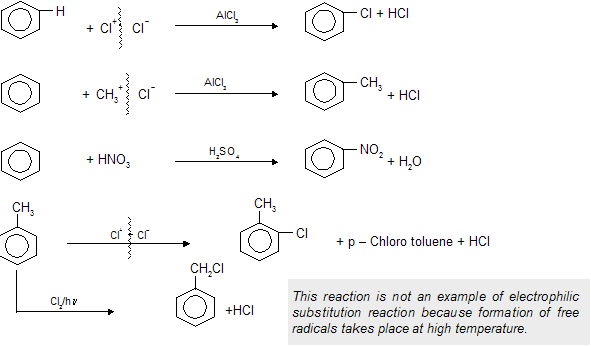
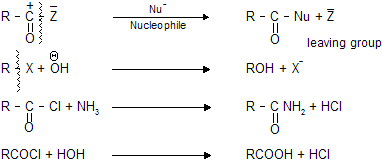
Weaker the base better the leaving group, due to which RCOCl is more reactive than RCONH2 , this property of leaving group is known as (FUGISITY)