fundamentals-of-organic-chemistry-3
(v) Elimination Reaction (Mechanism expressed in end of this chapter)
(a) Decarboxylation by soda lime [ NaOH + CaO] [Only applicable on acids & their derivatives ] removal
| of CO2 |  |
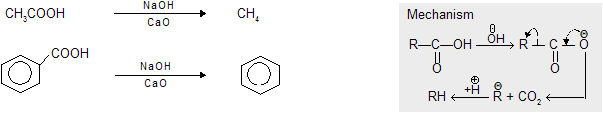
Methods to prepare higher to lower alkanes and vice versa
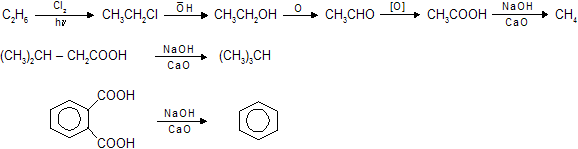
NaOH + CaO has no selective decarboxylation. So all the –COOH are removed in molecule.
(b) Dehydroyhalogenation -H X is removed using alcoholic KOH or strong bases as reagent.
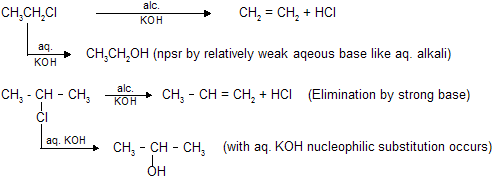
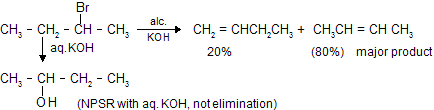
In this case CH3CH = CHCH3 is the major product. According to Saytzeff's rule more the alkyl groups are attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms, more is the stability of alkene. The hydrogen is taken out from the neighbouring carbon atom or the
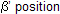 , by strong bases like alkoxides of metal.
, by strong bases like alkoxides of metal.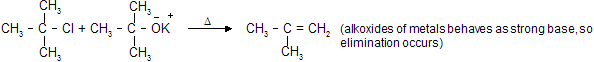
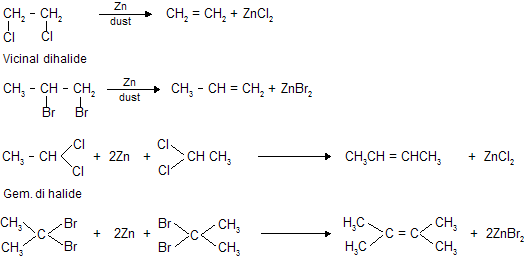
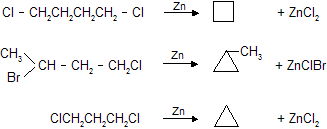
(c) Dehalogenation removal of halogen (- X2) by Zn dust.