Gas Laws - 5
Equating (i) to zero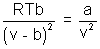
T = 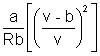
T = 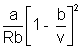
As v 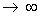
T 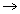 Tboyle’s
Tboyle’s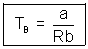
Critical parameter pertaining to its liquefication.
(1) Critical pressure (2) Critical Temperature (3) Critical Volume.
Critical PC: It is limiting value of pressure required for liquefication. If gas has pressure (P) less than PC it cannot be liquefied.
For liquefication
P 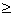 PC PC |
Critical TC: It is limiting value of temperature required for liquefication such that
T 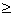 TC TC |
Critical VC: It is volume occupied by real gas at TC & PC.
There are calculated using Sudrew's critical
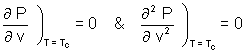
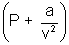 (v - b) = RT (n = 1)
(v - b) = RT (n = 1)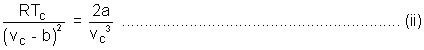
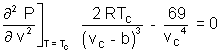
On
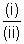 we get.
we get.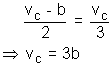
Putting VC = 3b in equation (ii)
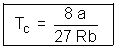
Putting value of TC & PC in (i)
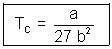
Easy Type:
Q.1. A balton balton filled with ideal gas is at sca surface & the taken depth of 100 m. What will its volume in terms of original volume ?
Ans: Pressure at surface = 76 cm of Hg = 76 x 13.6 cm of H2O
= 10.3 m of H2O
Dumb Question: Why 76 cm of Hg = 76 x 13.6 cm of H2O ?
Ans: Pressure =
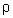 gh
ghheight of Hg = 76 cm & density = 13.6 g/cm3
Height of H2O = ? & density = 1 g/cm3
76 x 13.6 x
h = 76 x 13.6 cm of H2O
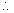 Pressure at 100 m depth = (100 + 10.3) m
Pressure at 100 m depth = (100 + 10.3) m10.3 x v = 110.3 x v2 => v2 = 0.093 v = 9.3 % of v
Q.2. A given mass of gas occupies 919 ml in dry state at STP. Same mass when collected once water at 150C & 750 mm pressure occupies 1 L. Calculate aq. tension (v - pressure) of water at 150C ?
Ans: Initial (at STP) Final
v1 = 919 ml v2 = 1000 ml
P1 = 760 mm P2 = ? (dry state)
T1 = 273 K T2 = 273 + 15 = 288 K
By
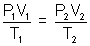
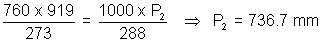
V.P. of water = Pressure of moist gas - P(dry gas)
= 750 - 736.7 = 13.3 mm
Q.3. Two vessels of capacitis 1.5 L & 2 L containing H2 at 750 mm & O2 at 100 mm respectively are connected to each other through a valve. What will be final pressure of gaseous mixture ?
Ans: Final volume = 1.5 + 2 = 3.5 L
For partial pressure of H2, P1V1 = P2V2
i.e. 750 x 1.5 = P2 x 3.5
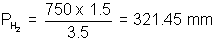
For O2, 100 x 2 = Po2 x 3.5 => Po2 = 57.14 mm
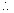 Pmix = Po2 +
Pmix = Po2 + 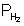 = 57.14 + 321.43
= 57.14 + 321.43= 378.57 mm
Question: Calculate diameter of O2 molecules.
Ans: b = 4v => v = b/4 = 7.95 x 10-3 L mol-1
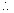 Volume occupied by 1 O2 molecule =
Volume occupied by 1 O2 molecule = 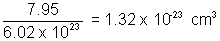
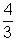 ITr3 = 1.32 x 10-23
ITr3 = 1.32 x 10-23on solving r = 2.932 A0
Q.5. 5g C2H6 are in a bulb of 1 L capacity. Bulb is burst if pressure exceeds 10 atm. At what temperature will be pressure of gas reach bursting value ?
Ans: Let bulb burst at TK0
PV = nRT i.e. PV =
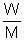 RT
RT10 x 1 =
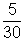 x 0.082 x T (Mol. mass of C2H6 = 30)
x 0.082 x T (Mol. mass of C2H6 = 30)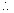 T = 730.81 K
T = 730.81 KQ.6. O2 is present in 1 L flask at a pressure of 7.6 x 10-10 mm of Hg. Calculate no. of O2 molecules at 00C.
Ans: PV = nRT
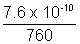 x 1 = n x 0.0821 x 273
x 1 = n x 0.0821 x 273n = 4.46 x 10-14 mole of O2
 No. of molecules of O2 = 4.46 x 10-14 x 6.023 x 1023
No. of molecules of O2 = 4.46 x 10-14 x 6.023 x 1023= 2.68 x 1010
Ans: P =
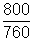 atm, T = 273 + 100 = 373 K
atm, T = 273 + 100 = 373 KLet density be d for CO2
For CO2 PV =
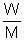 RT
RTPM =
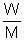 RT => PM = d RT
RT => PM = d RT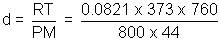 = 1.5124 g/L
= 1.5124 g/LQ.8. Pure O2 diffuses through aperture in 224 seconds, whereas mix. of O2 & another gas containing 80% O2 diffuses from same in 234 sec. What is mol. wt. of gas ?
Ans: For gaseous mix. 80% O2 (Mm) =
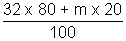 ................ (i)
................ (i)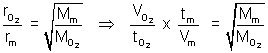
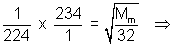 Mm = 34.92
Mm = 34.92Putting Mm
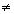 34.92
34.92We get, Mol wt. of gas m = 46.6
Q.9. Under 3 atm, 12.5 L of certain gas meighs 15g. Calculate avg. speed of gaseous molecules.
Ans: For gas PV =
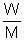 RT
RT3 x 12.5 = 15/M x 0.0821 x T => T/M = 30.45
uav =
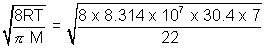 = 8.028 x 104 cm/s
= 8.028 x 104 cm/s