Gas Laws - 7
Q. ends. Its lies …… sum containg Hg & two equal ends containing air at same pressure Po. When tube is held at < 600 with vertical, length of air column above & below mercury are 46 & 44.5 cm respectively. Calculate pressure Po in cm of Hg.
Ans:
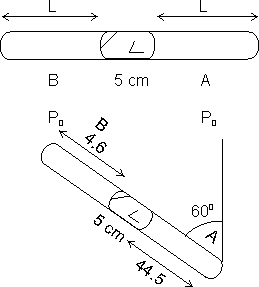
Let ......., length of air column is L cm.
2L + 5 = 45 + 5 + 44.5
L = 45.25 cm
When tube is held vertically at 600, Hg will dispalce to lower end.
PB + 5 cos60 = PA ................................... (i)
Dumb Question: Why equation (i) holds ?
Ans: Pressure at lower end is equal to pressure at upper end plus effective pressure due to mercury.
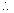 PA - PB = 5 x
PA - PB = 5 x  = 2.5 cm of Hg ............................... (i)
= 2.5 cm of Hg ............................... (i)For end A:
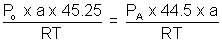
=> PA =
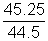 x Po ........................................... (ii)
x Po ........................................... (ii)For end B:
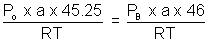
=> PB =
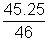 x Po .......................................... (iii)
x Po .......................................... (iii)By equation (i), (ii) & (iii)
Po = 75.4 cm of Hg.
Q. are filled to pressure of 2 atm, one with 14 Kg N2 & other with 1 Kg of H2. N2 ballon leaks to pressure of
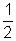 atm in 1 for. How long will it take for H2 balloon to reach a pressure of
atm in 1 for. How long will it take for H2 balloon to reach a pressure of 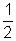 atm ?
atm ?Ans: At constant V & T, for a gas P
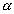 W
WDumb Question: How P
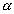 T at constant V & T ?
T at constant V & T ?Ans: PV = nRT
As V & T or constant
P
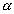 n => P
n => P 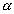
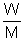
=> P
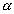 W (
W (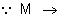 Mol. Mass)
Mol. Mass)For N2, P1 = 2 atm P2 =
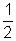 atm time t = 1 hr
atm time t = 1 hrW1 = 14 Kg, W2 = ?
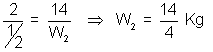
wt. of N2 deffused =
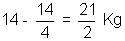
For H2, P1 = 2 atm, P2 =
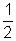 atm, t = t hr
atm, t = t hrW1 = 1 kg, W2 = ?
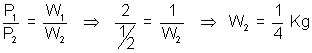
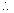 Wt. of H2 diffused = 1 -
Wt. of H2 diffused = 1 - 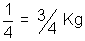
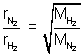
Moles of H2 diffused =
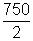
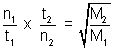
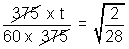
t = 60 x
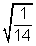 = 16 mus.
= 16 mus.Keywords:
* Boyle's Law
* Charle's Law
* Avogrado's Law
* Ideal Gas Equation
* Dalton's Law
* Aqueous Tension
* Partial Pressure
* Graham's Law
* Diffusion/Effusion
* Kinetic Gas Equation
* Most Probable Speed
* Root mean Square Speed
* Average Speed
* Compressibility factor
* Vander Waal's Equation
* Critical Temperature
* Critical Pressure
* Critical Volume