METALLURGY - 4
(iii) Zone refining of Fractional crystallisation : Elements such as Si, Ge, Ga, etc., Which are used as semi-conductors are refined by this method. Highly pure metals are obtained. The method is based on the difference in solubility of impurities in molten and solid state of the metal. A movable heater is fitted around a rod of the impure metal. The heater is slowly moved across the rod. The metal melts at the point of heating and as the heater moves on from one end of the rod to the other end, the pure metal crystallises while the impurities pass on the adjacent melted zone.
Summary of the Extraction of Metals
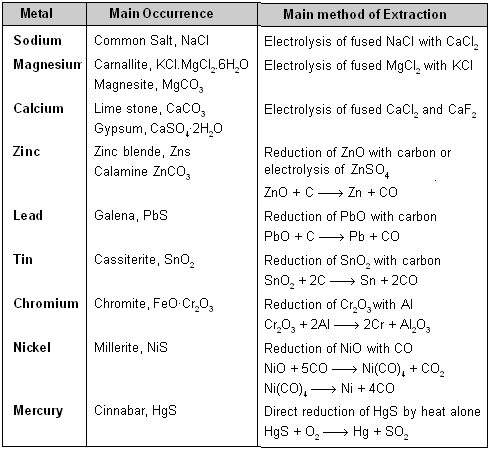
Different metallurgical processes can be broadly divided into three main types.
(i) Pyrometallurgy : Extraction is done using heat energy. The metals like Cu, Fe, Zn, Pb, Sn, Ni, Cr, Hg, etc., which are found in nature in the form of oxides, carbonates, sulphides are extracted by this process.
(ii) Hydrometallurgy : Extraction of metals involving aqueous solution is known as hydrometallurgy. Silver, gold, etc., are extracted by this process.
(iii) Electrometallurgy : Extraction of highly reactive metals such as Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al, etc., by carrying electrolysis of one of the suitable compound in fused or molten state.
FURNACES
Furnace is a device in which high temperature is produced either by burning a fuel or by using electricity. Several types of furnaces are used in the extraction of metals. The important ones are described below :
(i) Reverberatory furnace : This is the kind of a furnace in which fuel does not come in direct contact with the charge. The flames are deflected from the roof of the furnace to the charge undergoing reaction. Thus, this furnace can be used for reduction as well as for oxidation purposes.
The furnace consists of three main parts namely fire place, hearth and chimney. The fire place is built at one end of the furnace at slightly lower level than that of the hearth. The roof is made slanting and connects with the chimney on the other end. The hot gases from the fire place are reflected by the concave ceiling over the hearth. The furnace is surrounded on all sides by walls of fire bricks. Air supply can be controlled by vents and direct blast.
The furnace is used for smelting (reduction) and roasting of the ores. The reduction is done by the use of some suitable reducing agent. The furnace is used (a) for reducing the roasted tin stone (SnO2) to molten tin metal by the use
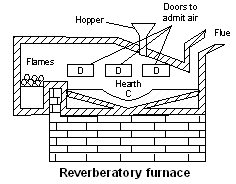
of
 coke (b) for roasting the galena ore (PbS) as to convert it into PbO and PbSO4 by the use of air (c) for roasting of copper pyrites (CuFeS2) as to convert it into Cu2O and FeO by means of air.
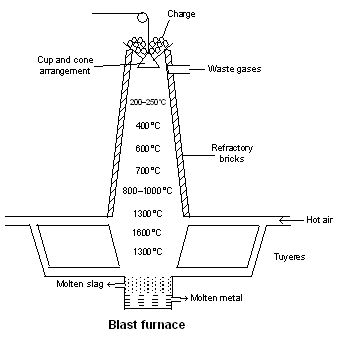
coke (b) for roasting the galena ore (PbS) as to convert it into PbO and PbSO4 by the use of air (c) for roasting of copper pyrites (CuFeS2) as to convert it into Cu2O and FeO by means of air.(ii) Blast furnace : It is a huge chimney like structure which can be between 25 and 60 meters in height and 5 to 10 metres in diameter. It is constructed of steel plates and the inner regions lined with fire-bricks. It has a double cup and cone arrangement at the top for the introduction of charge. Preheated air at a temperature of about 600°C is injected into the furnace through a number of pipes called tuyeres in the bottom of the furnace. It is provided with two tap holes plugged with clay; molten metal is tapped from the lower one and molten slag from the other. The temperature range in the furnace is from 1500°C at the bottom and 200–300°C at the top. Carbon and carbon monoxide reduce the metallic oxides to the free metals.
Blast furnace is frequently used for the extraction of iron and copper from their ores. Slag formation plays an important role in the blast furnace as it covers the melted metal and thus protects the metal from being reoxidised.
(iii) Muffle furnace : This furnace is used when high temperature is required and the fuel and its products of combustion are not to be desired to come into contact with the material to be heated. The muffle is a chamber made of refractory material. The muffle is surrounded by hot flames and hot gases all around. In an electric muffle furnace, the closed chamber is surrounded by heating electric coils. Such a furnace is used for the extraction of zinc, for annealing and gold and silver assaying.