Nucleus - 1
Introduction
Nucleus the central core of an atom is held together by a short -range force called nucleus force, which is also a potential source of energy called Nuclear energy. in this unit we will first understand the phenomenon of radioactivity and its explanation using bindingenergy concept. we will later study about the radioactive decay characteristcs which hold emmense temperature
in age estimation of old rocks etc.
Nuclear Characterstics:
(1) Nuclear mass: The total mass of nucleus in the nucleus is called as nucleus mass.
Nuclear mass =mass of proton + mass of neutron.
(2) Radius of Nucleus: Radius of Nucleus holds the relationship
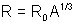 where R0 = 1.1 x 10-15m and A is mass number element.
where R0 = 1.1 x 10-15m and A is mass number element.(3) Nuclear charge:= Ze when Z=Mass number.
(4) Nuclear Density:
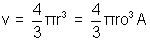
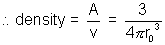
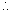 nucleus density is constant.
nucleus density is constant.Binding Energy of Nucleus:-
(1) the total energy Required to liberate all the nucleons from the Nucleus (i.e, to disintegrate the nucleus completely in to its constituent particles)
is called binding energy of the Nucleus.
(2) it has been observed experimentally that the mass of the nucleus is always less than the sum of masses of its constituent when measured in free state.
(3) this decrease in mass has been converted in to energy binding the Nucleus together.
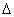 E =
E =  mc2
mc2where
 E = binding energy of nucleus.
E = binding energy of nucleus. m = mass defect = (mass of proton + mass of neutron) - (mass of nucleus)
m = mass defect = (mass of proton + mass of neutron) - (mass of nucleus)binding energy curve:
(1) Experssion for binding energy per nucleon: higher is the binding energy per nucleon more stable is the nucleus.
 m = Zmp+ (A - Z)mn - m
m = Zmp+ (A - Z)mn - mwhere mp, mnand m are masses of proton, neutron
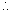 total binding energy of nucleus
total binding energy of nucleus E =
E =  mc2 = [zmp + (A - z)mn - m]xc2
mc2 = [zmp + (A - z)mn - m]xc2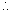 Mean binding energy per nucleon =
Mean binding energy per nucleon = 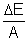 E. here mass m of nucleus is to be determined experimentally.
E. here mass m of nucleus is to be determined experimentally.Binding energy curveA graph between the binding energy per Nucleon and the mass number of nucleus is called as the binding energy curve
Few observation from this curve:
(a) Binding energy per nucleon is maximum(
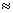 8.8 MeV) for nucleus having mass number 56. So 'Fe' is mass stable.
8.8 MeV) for nucleus having mass number 56. So 'Fe' is mass stable.(b) the light nucles with A < 20 are least stable.
(c) curve has peaks indicating much more stability of atoms like
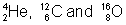
Nuclear fission:-
(1) The phenomenon of breaking a heavy nucleus in to two light nuclei of almost equal masses along with the release of huge amount of energy is called nuclear fission.
(2) The heavy atoms like uranium (which low binding energy per nucleon) undergo fission reaction to produce two stable nucleii and generate mass defect which convers in to energy
e.g
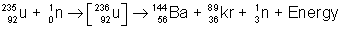
Dumb Question:
in which form is the energy released.
ans: Energy is released in the form of kinetic energy of fission fragments
some of the energy is also released in the form of r-rays, heat energy, sound energy and light energy.