Dumb question - Why probability of P(A/B
0) and P(A/B
1) is zero ?
Ans - Because in event we are getting 2 white ball.
and when in sample we have none or one white we can not get 2 white ball.
Stockist approach :-
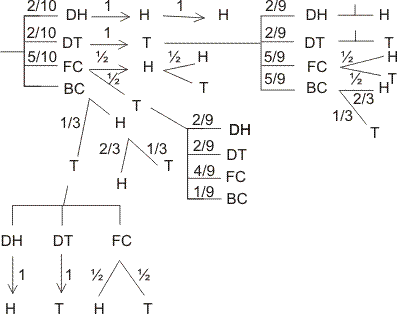
Q- A bag contains 5 fair coin, 2 doulaly headed coin, 2 doubly tailed and are biased coin. Probability of head with biased = 2/3 . A coin is selected and tossed. If head appeared same coin is tossed and if tail appears another coin selected from remaining and tosed. Find the chasce -
(1) Same .coin is tessed twice .
(2) Chance .head appears in both toss.
(3)If head appears in both wins. find the chance that it is doubly headed coin .
Ans - Total coin = 5 + 2 + 2 + 1 = 10
(1) P(getting H in I
st toss) =
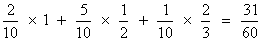
(2) P(getting both (H H) in 2 toss) =

(3) P(Doubly head / H H )

=
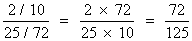 In finite samble space (Geometrical probaility )
In finite samble space (Geometrical probaility ) :-
(1) If a point is randomly sclected from area 'S' which indudes an area 6 then chance that it is sclected from area 6
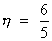
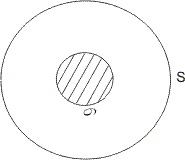
(2) If a point is randomly taken from line AB of length L then chance that it is selected from the segment PQ(l) contained by AB is = l/2
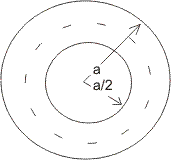
Illustration :- In a circle of radius 'a'. Find the probalility that point is close to the circumference than to its centre.
Ans - n(S) =

E : Point is close to circumference than oits centre.
P(E) =

 Dumb question
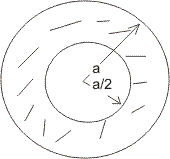
Dumb question - How probability of " point is close to circumference than its centre " is 3/4 .
Ans - A point is close to circumference than its centre when it lies in region of outside the circle of r = a/2 and inside the circle of r = a .
P(E) =
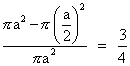
 Easy levelQ. 1
Easy levelQ. 1 - A natural no. is randomly selected. Find the chance that digit in unit place of its square is 4.
Ans :-
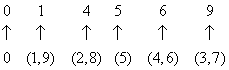
There are only two digit (2 and 8). Whose square's unit place is 4.
So, P(E) = 2/10 = 1/5
Q. 2 4 red and 3 white ball are arranged | n a row. Find chance that two ball at extreme are whit .
Ans :-
Case I:- alike balls

n(S)=
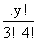
n(A)=

P(A)=
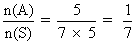 Case
Case2:- Different balls-
n(S) = 7!
n(A) = 3C
2. 2!, 5!
P(A) =
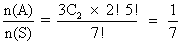 Q. 3
Q. 3- P(A) = 1/2 ,P(B) = 1/2 . Find the least and greatest valume of intersection P(A img B).
Ans - P(A
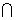
B) = P(A). P(B/A)
P(A

B) greatest = 1/2 if P(B/A) = 1

=
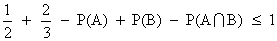
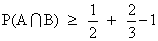
 Q. 4
Q. 4- A and B are independent then show that
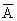
and

are also independent .
Ans -
Note - If and are independent. then
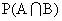
P(A) . P(B)
T.PT :-
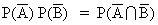 L. H. S.
L. H. S. :-

{ 1 - P(A) } { 1 - P(B)}
= 1 - P(A) - P(B) + P(A) . P(B)
= 1 - [P(A) + P(B) - P(A

B)]
= 1 - P(A

B)
= P (
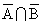
)
Q. 5 - Two cords are drawn from 52 cards pack. Find the chance that both the cards are aces.
Ans- n(S) = no. of ways drawing 2 cards from 52 cards.
= 52 C
2n(A) = no. of ways drawing 2 ace cards from 4 ace card
= 4 C
2P(E) =
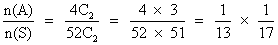
P(E) =
