Q. 3- Three whole no. is selected at random and multipliea find the chance that-
(1) Their product is divisible by 5 but not 10.
(2)Divisible by 10 .
(3) is an even no.
Ans- E
1 
Digits at unit plce of 3 whole no. 1, 3, 7, 9
E
2 
digits at unit place of whole no. is 1, 3, 5, 7, 9
E
3 
digits at unit place of 3 whole no;s is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 there are 10 digits -
P(E
1) =
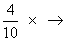
I
st Whole no. ,
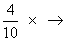
2
nd Whole no.,
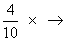
3
rd Whole no., =
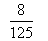
P(E
2) =
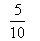
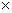
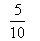
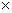
=
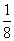
P(E
3) =
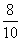
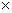
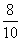
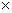
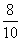
=
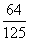
divisible by 5 not by 10
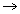
at unit place only 5 is there .
(1) P(divisible by 5 not by 10 ) = P(E
2) - P(E
1)
=
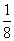
-
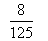
=
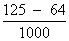
=
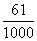
(2) (divisible by 10 means last digit is zers )
= 1 -
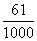
-
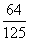
=
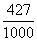
Dumb question -
Q. How P(disivible by 5 not by 10 ) = P(E
2) - P(E
1)
Ans- Divisible by 5 not 10 only when at uniy place only 5 is there.
P(E
1) = Prob. of having 1, 3, 7, 9 at unit place
P(E
2) = Prob. of having '5' at unit place
= P(E
2) - P(E
1)
=P (divisible by 5 not by 10)
(3) P(even) = 1 - P(E
2) [ have digit 2, 4, 6, 8 at unit place ]
= 1 -
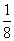
=
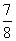 Key words
Key words• Sample space
• Equally likely events
• Mutually exclusive events
• Exhaustive events
• Independent events
• Expectation value
• Bernoulli's trial
• Boye's theorem (Total frobability theorem)
• Infinite sample space.